Deploy Self-hosted Retool on Amazon EC2
Learn how to deploy Self-hosted Retool on Amazon EC2 with Docker Compose.
Self-hosted Retool is available on an Enterprise plan only.
You can deploy Self-hosted Retool on Amazon EC2 with Docker Compose.
Requirements
To deploy Retool, you need:
- A Retool license key, which you can obtain from the Retool Self-hosted Portal or your Retool account manager.
- Familiarity with and installations of Docker Engine and Docker Compose.
- A compatible Linux-based virtual machine.
- An externally managed PostgreSQL database for use by the deployment.
In addition, Retool recommends you:
- Follow this guide using an administrative, non-Root AWS user.
- Manage your service quotas for your Retool deployment's AWS Region as you scale.
VM configuration
Self-hosted Retool instances require a Linux-based virtual machine that meets the following requirements:
- Ubuntu 22.04 or later.
- x86 architecture.
- 16GiB memory.
- 8x vCPUs.
- 60GiB storage.
curlandunzipsoftware packages installed.
Retool recommends you allocate more resources than the minimum requirements so that your instance can more easily scale.
Temporal
Temporal is a distributed system used to schedule and run asynchronous tasks for Retool Workflows and Retool Agents. A Self-hosted Retool instance uses a Temporal cluster to facilitate the execution of each workflow amongst a pool of self-hosted workers that make queries and execute code in your VPC. Temporal manages the queueing, scheduling, and orchestration of workflows to guarantee that each workflow block executes in the correct order of the control flow. It does not store any block results by default.
You can use a Retool-managed cluster on Temporal Cloud, which is recommended for most use cases. You can also use an existing self-managed cluster that is hosted on Temporal Cloud or in your own infrastructure. Alternatively, you can spin up a new self-hosted cluster alongside your Self-hosted Retool instance.
- Retool-managed cluster
- Self-managed cluster
- Local cluster
Recommended
You should use a Retool-managed cluster if:
- You are on a version greater than 3.6.14.
- Your organization is committed (under contract) on a Business or an Enterprise plan.
- You don't have an existing cluster which you prefer to use.
- Your cluster only needs to be used for a Self-hosted Retool deployment.
- You don't want to manage the cluster directly.
- You have a single or multi-instance Retool deployment, where each instance requires its own namespace.
Retool admins can enable Retool-managed Temporal. To get started, navigate to the Retool Workflows page and click Enroll now. Once you update your configuration, return to the page and click Complete setup.
It can take a few minutes to initialize a namespace in Retool-managed Temporal.
Retool-managed Temporal Clusters are hosted on Temporal Cloud. Your Self-hosted Retool deployment communicates with the cluster when building, deploying, and executing Retool Workflows. All orchestration data to Temporal is fully encrypted and uses the private encryption key set for your deployment.
If you want to create a new, self-hosted cluster on Temporal Cloud, sign up first. Once your account is provisioned, you can then deploy Self-hosted Retool.
Temporal Cloud supports 10+ AWS regions from which to select, 99.99% availability, and 99.99% guarantee against service errors.
You should use an existing self-managed cluster, hosted on Temporal Cloud or in your own infrastructure, if:
- You cannot use a Retool-managed cluster.
- You are on a version earlier than 3.6.14.
- Your organization is self-serve, or on the Free, Team, or Business plan.
- You have an existing cluster and would prefer to use another namespace within it.
- You need a cluster for uses other than a Self-hosted Retool deployment.
- You want to manage the cluster directly.
- You have a multi-instance Retool deployment, where each instance would have its own namespace in a shared Self-hosted Temporal Cluster.
Self-managed cluster considerations
Retool recommends using a separate datastore for the Workflows Queue in production. Consider using AWS Aurora Serverless V2 configured to an ACU (cpu) provision ranging from 0.5 to 8 ACU. 1 ACU can provide around 10 QPS. The Workflows Queue is write-heavy (around 100:1 write to read operations) and Aurora Serverless can scale to accommodate spikes in traffic without any extra configuration.
Environments
For test environments, Retool recommends using the same database for the Retool Database and Workflows Queue. Without any extra configuration, Retool Workflows can process approximately 5-10 QPS (roughly, 5-10 concurrent blocks executed per second).
Workflows at scale
You can scale Self-hosted Retool Workflow-related services to perform a high rate of concurrent blocks per second. If your deployment needs to process more than 10 workflows per second, you can use:
- A Retool-managed cluster.
- A self-managed cluster on Temporal Cloud.
- Apache Cassandra as the Temporal datastore.
If you anticipate running workflows at a higher scale, please reach out to us to work through a deployment strategy that is best for your use case.
You should spin up a new cluster alongside your Self-hosted Retool instance if:
- You cannot use a Retool-managed cluster.
- You are on a version greater than 3.6.14.
- Your organization is on the Free, Team, or Business plan.
- You don't have an existing cluster to use.
- You don't need a cluster for uses other than a Self-hosted Retool deployment.
- You want to test a Self-hosted Retool deployment with a local cluster first.
- You have a multi-instance Retool deployment, but each instance is in its own VPC and requires its own Self-hosted Temporal Cluster.
Local cluster considerations
Retool recommends using a separate datastore for the Workflows Queue in production. Consider using AWS Aurora Serverless V2 configured to an ACU (cpu) provision ranging from 0.5 to 8 ACU. 1 ACU can provide around 10 QPS. The Workflows Queue is write-heavy (around 100:1 write to read operations) and Aurora Serverless can scale to accommodate spikes in traffic without any extra configuration.
Environments
For test environments, Retool recommends using the same database for the Retool Database and Workflows Queue. Without any extra configuration, Retool Workflows can process approximately 5-10 QPS (roughly, 5-10 concurrent blocks executed per second).
Workflows at scale
You can scale Self-hosted Retool Workflow-related services to perform a high rate of concurrent blocks per second. If your deployment needs to process more than 10 workflows per second, you can use:
- A Retool-managed cluster.
- A self-managed cluster on Temporal Cloud.
- Apache Cassandra as the Temporal datastore.
If you anticipate running workflows at a higher scale, please reach out to us to work through a deployment strategy that is best for your use case.
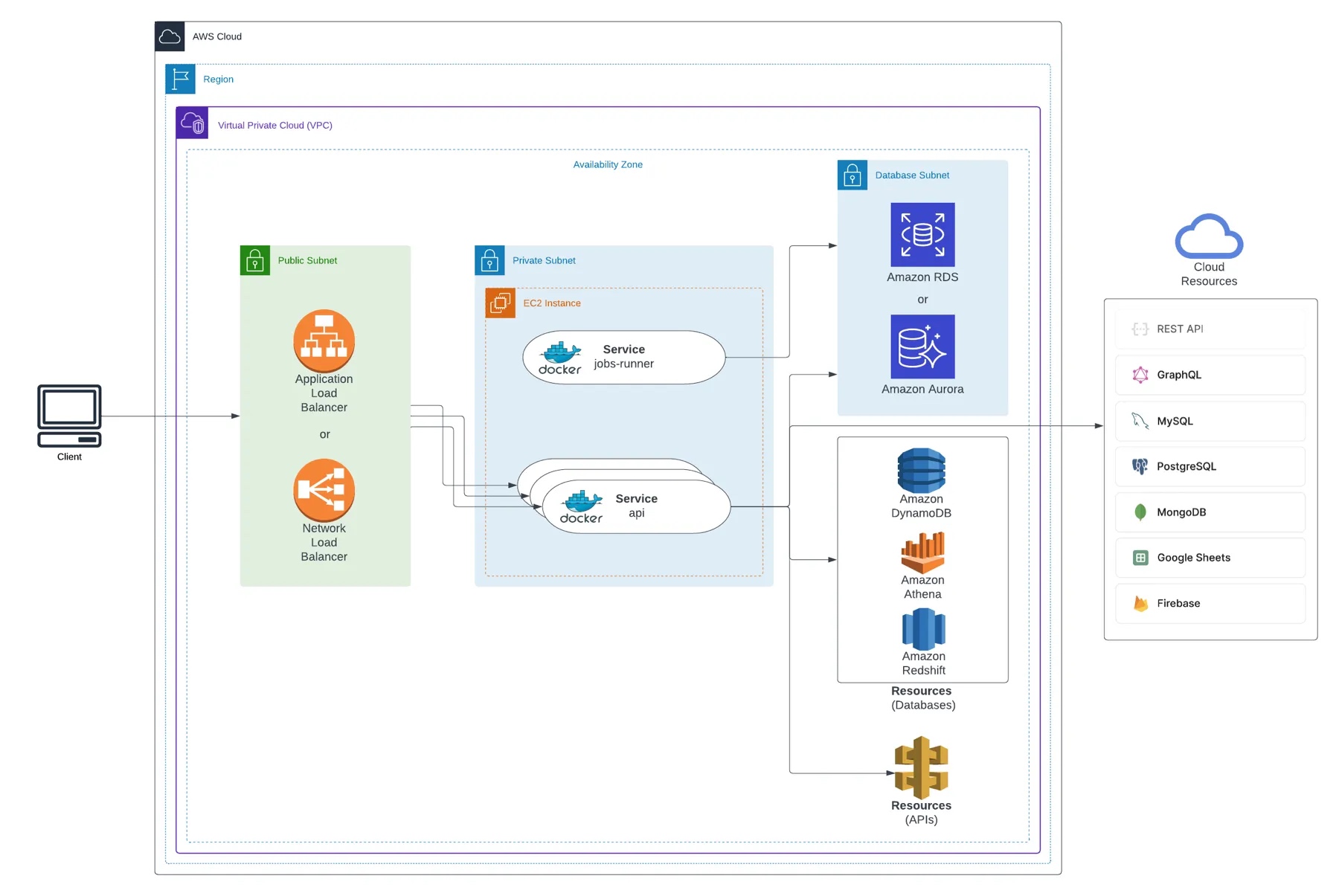
System architecture
The following diagram shows the resulting system architecture for your deployment.
1. Create a Linux EC2 instance
Create a new Linux EC2 instance in the Amazon EC2 console using an Amazon Machine Image (AMI) that meets the minimum requirements. Refer to the Amazon EC2 documentation to learn how to create a new instance.
| VM setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Authentication | Enable SSH public key authentication and provide a username. Generate a new key-pair and specify a name. |
| Network | Create or use an existing security group to configure rules for SSH (22), HTTP (80), HTTPS (443), and Custom TCP (3000). The source for these rules must be 0.0.0.0/0 and ::/0. |
Self-hosted Retool initially runs on port 3000. Once SSL is configured, this port is no longer required.
2. Download Self-hosted Retool
You can connect in the AWS console using EC2 Instance Connect, or on the command line using an SSH client, with the SSH key pair you selected in your EC2 dashboard.
ssh -i keypair.pem <username>@<public_ip>
Download or clone the retool-on-premise GitHub repository.
curl -L -O https://github.com/tryretool/retool-onpremise/archive/master.zip \
&& unzip master.zip \
&& cd retool-onpremise-master
git clone https://github.com/tryretool/retool-onpremise.git
3. Install Docker dependencies
Run ./install.sh to prepare the Docker image. The script also installs Docker and Docker Compose if they are not already available.
4. Back up encryption key
The install script generates a value for ENCRYPTION_KEY and stores it within docker.env. This key encrypts secrets for your Retool resources.
Save this key in a secure location outside of Retool.
You will need to reconfigure all resources if the encryption key is lost.
5. Configure the instance
There are three files to configure for your deployment:
| File | Description |
|---|---|
Dockerfile | The standard configuration file for Retool's Docker image. |
compose.yaml | The Docker Compose configuration to use for the deployment. |
docker.env | Environment variables to control or override certain deployment options. |
Specify the version of Retool to use
In the Dockerfile, specify the Docker tag for the version of Retool to install, such as tryretool/backend:3.300.9-stable.
Specify the exact version to use, such as 3.300.9-stable. This ensures you know exactly which version will be deployed.
Prepare Compose file
The default Docker Compose configuration includes a Temporal container that enables the use of Retool Workflows. To instead use a Retool or self-managed Temporal Cluster, comment out the include block in compose.yaml, and update the WORKFLOW_TEMPORAL environment variables in docker.env.
- Retool-managed cluster
- Self-managed cluster
- Local cluster
Allow your deployment to connect to Temporal
Open up egress to the public internet on ports 443 and 7233 to allow outbound-only connections to Temporal Cloud from your deployment. This is so services can enqueue work to, and poll work out, of Temporal.
Temporal Cloud does not have a static IP range to allow list. If more specificity is required, egress is required on ports on the following domains:
| Port | Domains |
|---|---|
| 443 | *.retool.com, *.tryretool.com, *.temporal.io |
| 7233 | *.tmprl.cloud |
Follow the steps for configuring either a Temporal Cloud cluster or a self-hosted cluster in your VPC.
Temporal Cloud
Allow your deployment to connect to Temporal
Open up egress to the public internet on ports 443 and 7233 to allow outbound-only connections to Temporal Cloud from your deployment. This is so services can enqueue work to, and poll work out, of Temporal.
Temporal Cloud does not have a static IP range to allow list. If more specificity is required, egress is required on ports on the following domains:
| Port | Domains |
|---|---|
| 443 | *.retool.com, *.tryretool.com, *.temporal.io |
| 7233 | *.tmprl.cloud |
Configure environment variables for Temporal Cluster
Set the following environment variables for the MAIN_BACKEND, WORKFLOW_BACKEND, and WORKFLOW_TEMPORAL_WORKER services in the configuration file.
Temporal Cloud requires security certificates for secure access.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
WORKFLOW_TEMPORAL_CLUSTER_NAMESPACE | The namespace in your Temporal Cluster for each Retool deployment you have (e.g., retool-prod). Default is workflows. |
WORKFLOW_TEMPORAL_CLUSTER_FRONTEND_HOST | The frontend host of the cluster. |
WORKFLOW_TEMPORAL_CLUSTER_FRONTEND_PORT | The port with which to connect. Default is 7233. |
WORKFLOW_TEMPORAL_TLS_ENABLED | Whether to enable mTLS. Set to true. |
WORKFLOW_TEMPORAL_TLS_CRT | The base64-encoded mTLS certificate. |
WORKFLOW_TEMPORAL_TLS_KEY | The base64-encoded mTLS key. |
Self-hosted
If you use a PostgreSQL database as a persistence store, the PostgreSQL user must have permissions to CREATE DATABASE. If this is not possible, you can manually create the required databases in your PostgreSQL cluster: temporal and temporal_visibility.
Configure environment variables for Temporal Cluster
Set the following environment variables for MAIN_BACKEND and WORKFLOW_TEMPORAL_WORKER services, if not already configured.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
WORKFLOW_TEMPORAL_CLUSTER_NAMESPACE | The namespace in your Temporal Cluster for each Retool deployment you have (e.g., retool-prod). Default is workflows. |
WORKFLOW_TEMPORAL_CLUSTER_FRONTEND_HOST | The frontend host of the Temporal Cluster. |
WORKFLOW_TEMPORAL_CLUSTER_FRONTEND_PORT | The port with which to connect to the Temporal Cluster. Defaults to 7233. |
WORKFLOW_TEMPORAL_TLS_ENABLED | (Optional) Whether to enable mTLS. |
WORKFLOW_TEMPORAL_TLS_CRT | (Optional) The base64-encoded mTLS certificate. |
WORKFLOW_TEMPORAL_TLS_KEY | (Optional) The base64-encoded mTLS key. |
Use the default values in the configuration.
Configure environment variables
Configure the following environment variables in docker.env:
| Variable | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
LICENSE_KEY | Your Self-hosted Retool license key. | The license key obtained from the Self-hosted Portal. |
COOKIE_INSECURE | true | Allows you to use Self-hosted Retool without SSL. This variable is included in docker.env for you to uncomment. |
BASE_DOMAIN | The deployment instance URL (e.g., https://retool.example.com). | The FQDN for the Retool instance being deployed. |
Once you configure SSL, set COOKIE_INSECURE to false.
6. Start the instance
Run sudo docker compose up -d to start Self-hosted Retool. This can take several minutes as the instance performs the initial setup and starts its services for the first time.
Once running, Self-hosted Retool is available at http://<your-ec2-ip-address>/auth/signup. When you first visit the page, you must create an admin account.
You can check whether Docker containers are running with sudo docker compose ps.
Additional configuration
You must prepare any self-hosted deployment instance for use in a production environment. Additional configuration may also be required depending on your needs.
The use of environment variables is often necessary to configure SSO, source control, and other self-hosted features.
SSL
Docker Compose deployments of Self-hosted Retool include https-portal to automatically configure HTTPS. Before you start using your deployment instance in production, you must configure SSL.
You can either provision a certificate with Let's Encrypt or manually add your own certificates.
Set COOKIE_INSECURE to false once you configure SSL.
Single sign-on (SSO)
Retool supports OpenID Connect (OIDC) and Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) identity providers. Organizations can map IdP roles to Retool permission groups using OIDC role mapping or SAML group sync. Retool also supports LDAP Google Group sync when using Sign in with Google.
Refer to the SSO quickstart for information on configuring IdP providers.
Source Control
Source Control allows organizations to manage changes to apps, workflows, resources, and themes using pull requests on remote source control management (SCM) providers, such as GitHub, GitLab, AWS CodeCommit, Bitbucket, and Azure Repos. Instead of making changes directly to an app, changes are made on a separate branch.
If you intend to use Source Control, Retool recommends configuring this as you prepare for production use to ensure that change management is in use from the start.
Update your EC2 instance
Follow these instructions to update your Retool instance to a newer release version.
Retool strongly recommends that you back up the VM before performing an update. If you cannot complete a full backup, you should at least:
- Create a snapshot of your PostgreSQL database.
- Copy the environment variables in
docker.envto a secure location outside of Retool.
To update your deployment to a newer version of Self-hosted Retool:
- Update the
Dockerfilewith the newer version number. For example:tryretool/backend:3.300.9-stable - If your deployment is using
CodeExecutor.Dockerfile, update it with the same version. - Run
./upgrade.shto perform the update.
The Retool instance is temporarily stopped while the update takes place and restarts automatically. Retool recommends performing the upgrade during off-peak hours to minimize downtime for users.