Evals in Retool Agents
Systematic tests using evals.
| Agents Availability | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud | Public beta | ||
| Self-hosted Edge 3.234 or later | Public beta | ||
| Self-hosted Stable 3.253 or later | Public beta | ||
Evals are systematic tests to assess large language models (LLMs) and agents on tasks like reasoning, accuracy, or safety. They use benchmarks or real-world scenarios to ensure models produce reliable, coherent, and ethical outputs.
When running an eval, Retool provides an input to the LLM. A reviewer scores the LLM output (0 to 1). Sometimes there are clear expected outputs (for example, programmatic reviewers like exact match), and sometimes expected outputs are less clear (for example, LLM as a judge reviewers like tone detection).
Eval runs count towards billable agent runtime. For more information about billing, refer to the Billing and usage page.
By tracking and scoring the results of your evals, you can test agents to determine if you've introduced breaking changes to an agent, you've improved the agent’s behavior, or if the agent is working as expected.
Evals tab
The Evals tab allows you to evaluate and compare agent runs. To evaluate your agent run, you must first add a Dataset, create a Test case, and add a Reviewer.
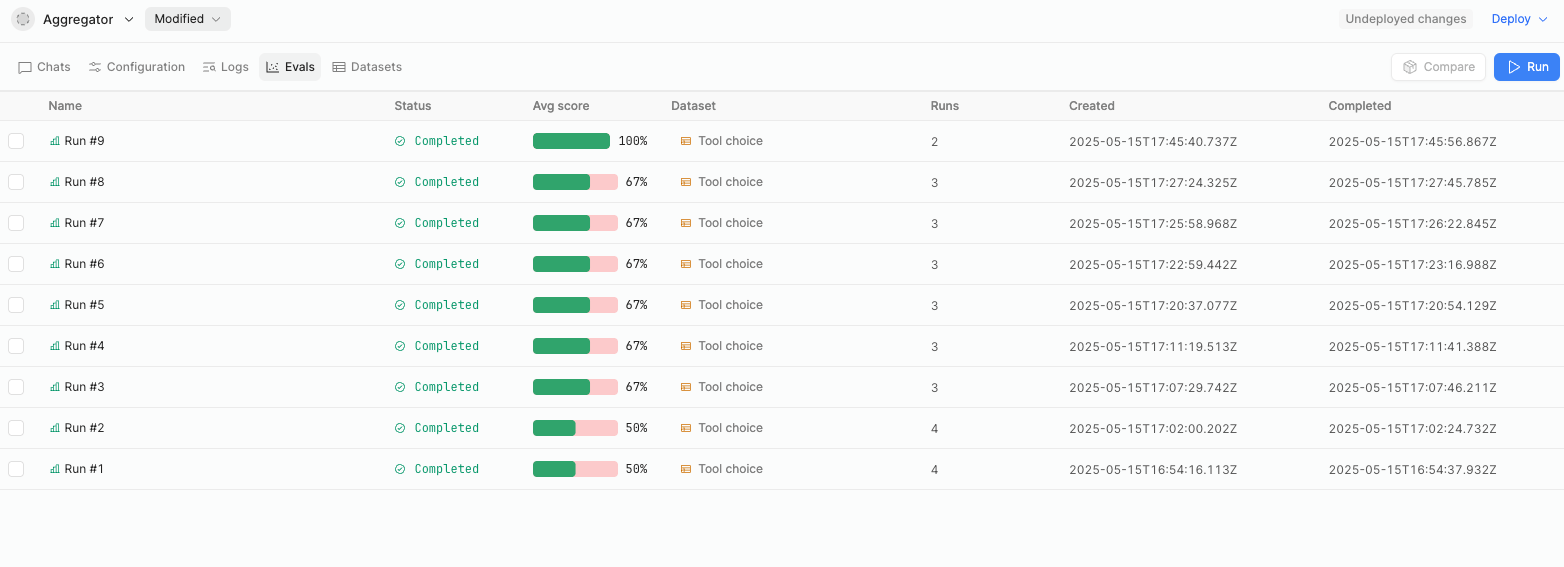
Retool Agents Evals tab.
You can compare two agent runs side-by-side by selecting the checkbox next to the Name of the runs you want to compare and clicking Compare. You cannot compare more than two runs at a time.
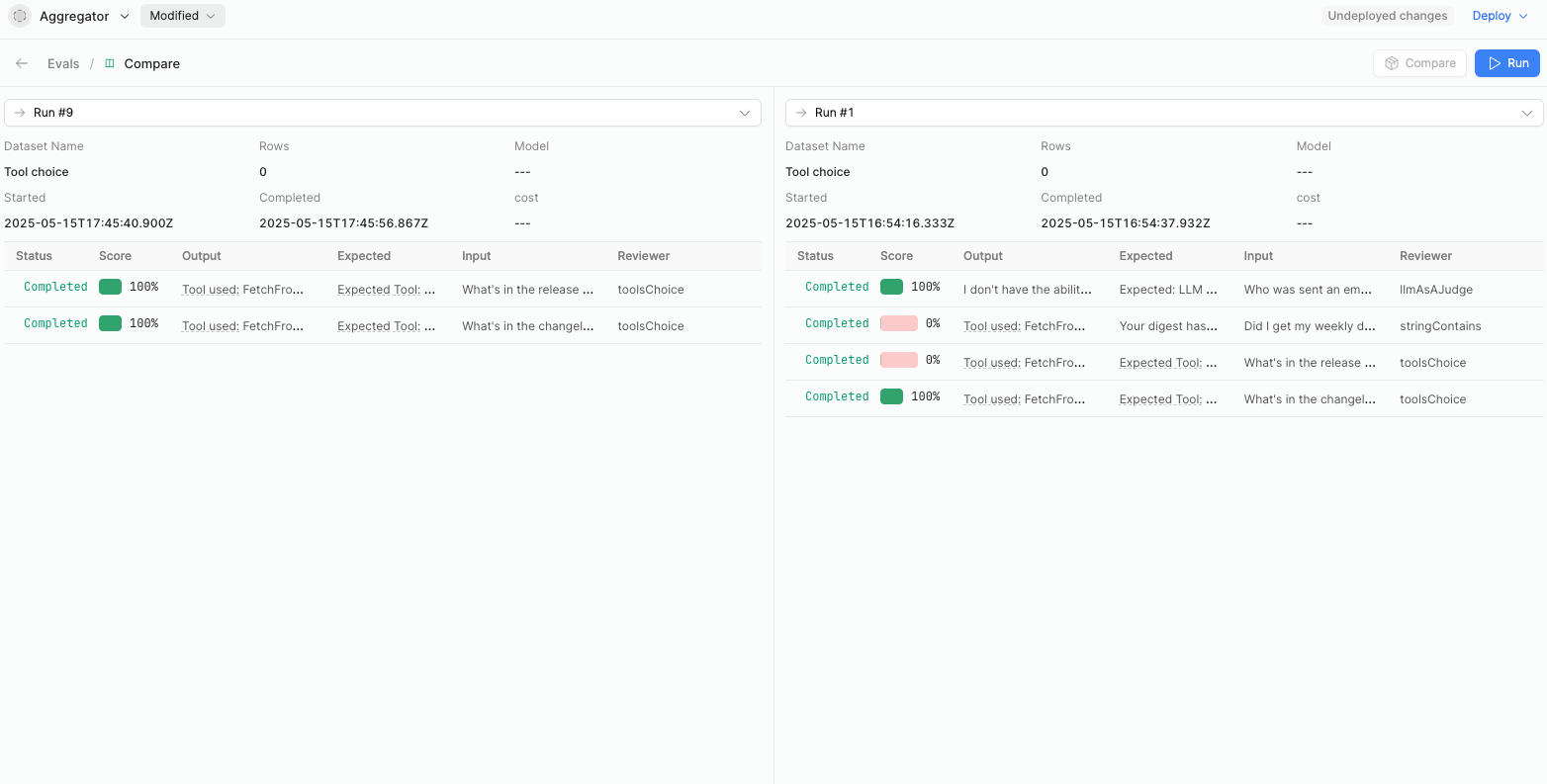
Evals comparison of two agent runs.
Datasets and test cases
A dataset is a collection of test cases.
A test case contains Input, which is provided to the LLM to prompt an answer. For example Schedule a meeting between Alice and Bob tomorrow. And the expected output is mapped to the two types of actions that an agent can take: choosing tools, or returning a final answer.
- When the test case Type is Tool choice, the evaluation verifies that the agent selects the Expected tool, and extracts the Expected parameters from the Input.
- When the test case Type is Final answer, the evaluation may verify metrics with a much broader set of Reviewers.
An agent may have many datasets for many test cases.
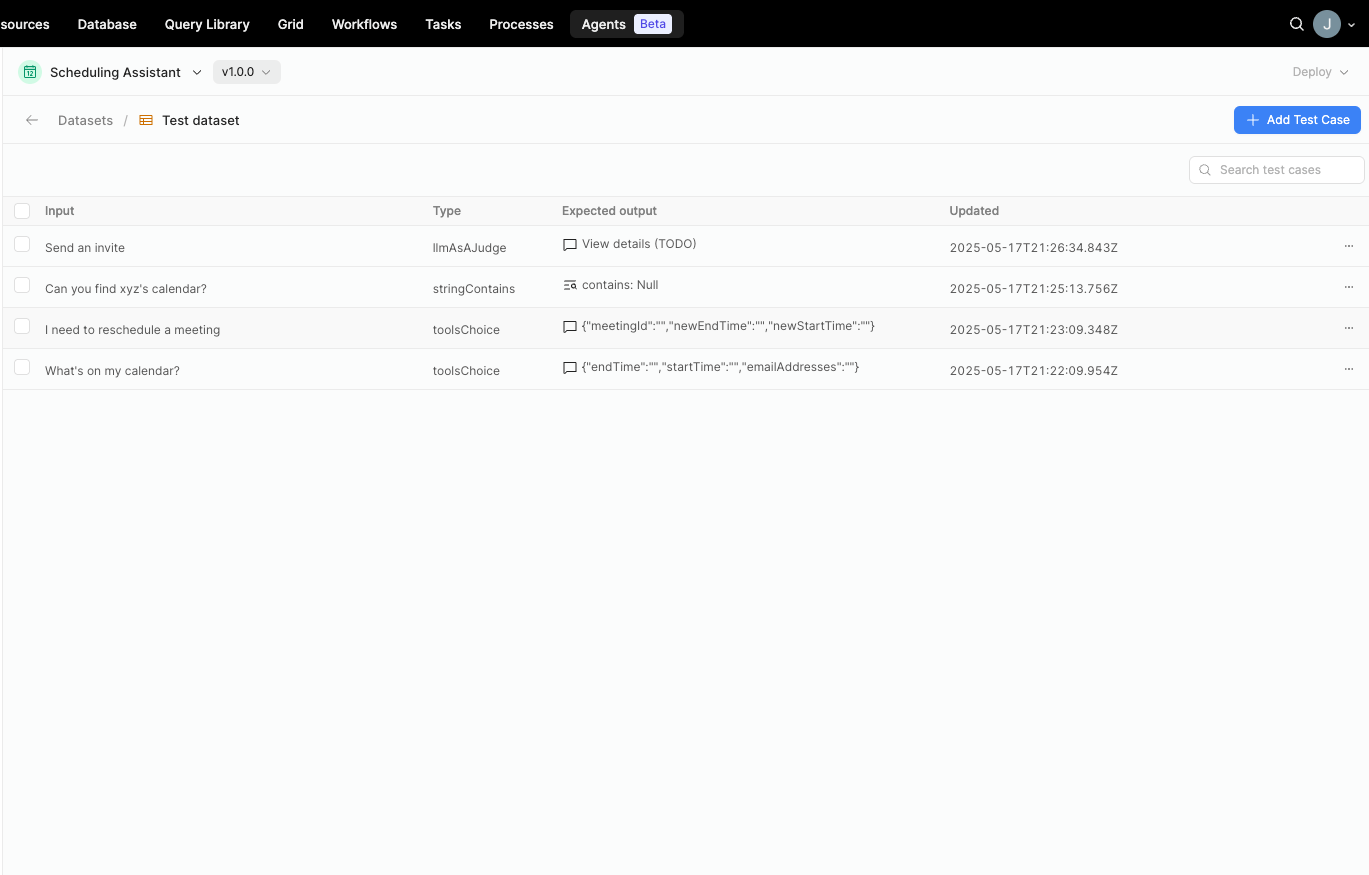
Example dataset with several test cases.
Reviewers
Reviewers score the correctness of the agent's output, and provide an explanation for the score. During the Eval run, a reviewer accepts the output from the LLM, parameters that vary based on the reviewer type selected, and returns a score beetween 0 and 1.
Retool provides Programmatic and LLM as a Judge preconfigured reviewers you can use to help evaluate your agent.
Programmatic
Programmatic reviewers use code to score output based on predefined rules. Use programmatic reviewers when you can clearly define the agent's expected output.
| Reviewer name | Description | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Exact match | Determines whether two values are the same. | None |
| Valid JSON | Evaluates the validity of the JSON output. | None |
| Valid XML | Evaluates the validity of the XML output. | None |
| String contains | Determines whether a string contains a certain value. | searchString - the search string to look up ignoreCase - ignore capitalization. |
| JSON Schema match | Determines whether the output of the agent is valid JSON conforming to the schema you specify. | JSON Schema - the format of your JSON schema. |
| Levenshtein | A similarity score based on the Levenshtein distance between two strings with the formula 1 - (lev / length of longer string) = similarity score. For example, the distance between Hello World and hello borld is 1 and the output of the reviewer is 0.91 | None |
LLM-as-a-judge
LLM-as-a-judge reviewers use an LLM to determine the agent's score based on what you define in the input Prompt and Choice score between 0 and 1. Use LLM as a Judge reviewers when the agent's expected output is not clearly defined.
| Reviewer name | Description | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Tone detection | Evaluates the tone of an agent's output based on the user input prompt. | Prompt Choice Scores |
| Factuality | Evaluates whether an output is factual. | Prompt Choice Scores |
| Closed QA | Evaluates whether an output answers the input. | Prompt Choice Scores |