Lightweight Extract Transform and Load (ETL) Process
The following lab covers how to perform Lightweight ETL on a CSV Batch API. Lightweight ETL focuses on smaller datasets (KB/MB) versus traditional ETL that processes (GB/PB). To demonstrate this, the lab will focus on using a simulated Batch API, storing the CSV response in Retool Storage, and then performing a bulk insert into Retool Database. The following solution design using Retool Iconography shows the sequence of steps.
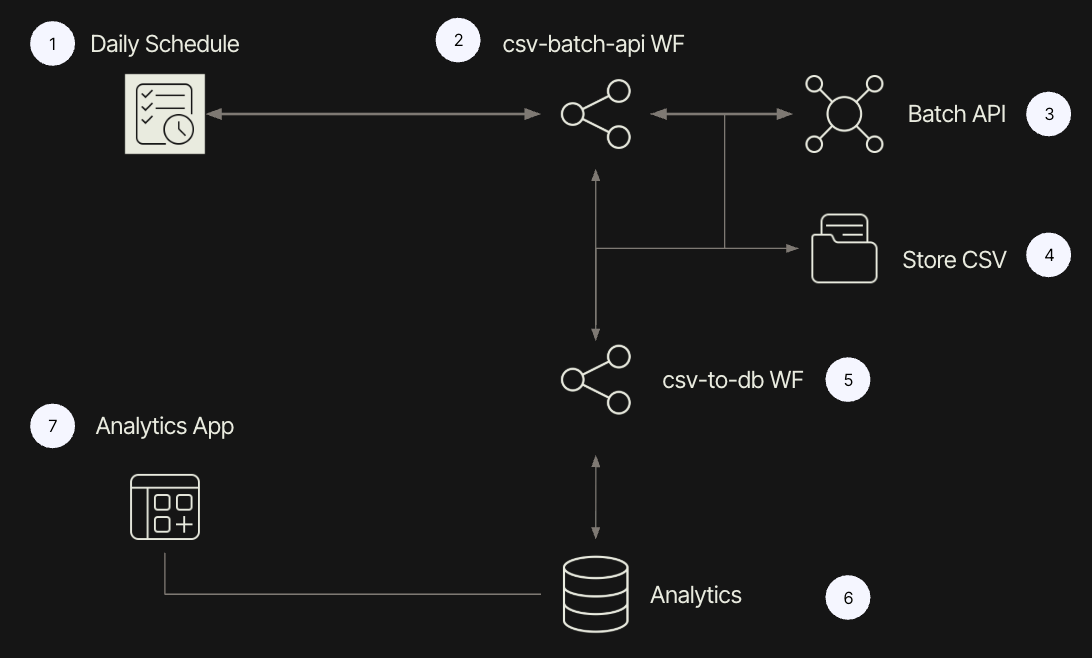
Overview of CSV Batch API
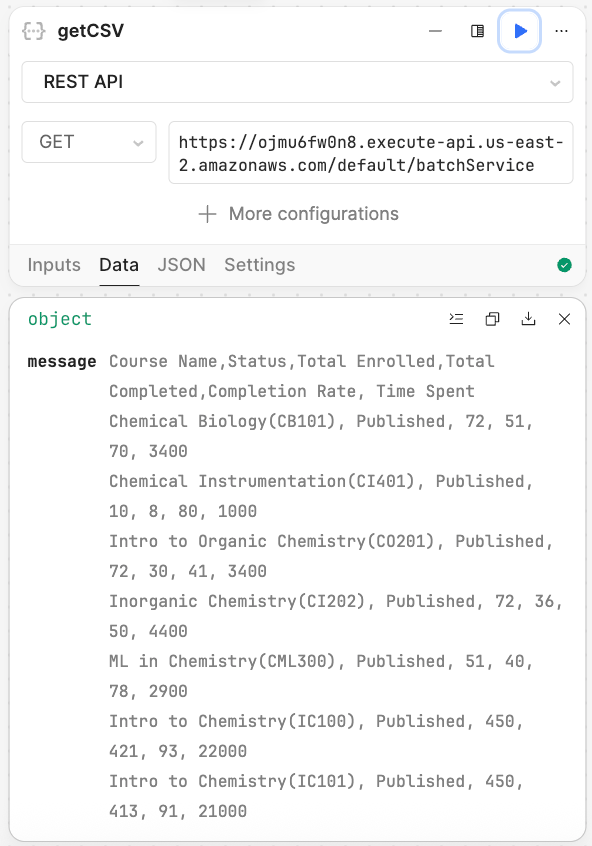
The simulated CSV Batch API provides a CSV output embedded within a JSON output.
Course Name,Status,Total Enrolled,Total Completed,Completion Rate, Time Spent
Chemical Biology(CB101), Published, 72, 51, 70, 3400
Chemical Instrumentation(CI401), Published, 10, 8, 80, 1000
Intro to Organic Chemistry(CO201), Published, 72, 30, 41, 3400
Inorganic Chemistry(CI202), Published, 72, 36, 50, 4400
ML in Chemistry(CML300), Published, 51, 40, 78, 2900
Intro to Chemistry(IC100), Published, 450, 421, 93, 22000
Intro to Chemistry(IC101), Published, 450, 413, 91, 21000
Examining the output, you will see enrollment for a university's chemistry department including course name, status of course, number of enrolled students, number of students that have completed the course, percentage of students completed, and time spent.
Steps
Create a labs folder in Retool Storage
This step creates a sub-folder in Retool Storage to store the CSV download file.
- Select Retool Home > Resources > Retool Storage > New Folder
- Specify a folder name of
labsand select Create folder.
Create csv-batch-api workflow
This step uses a scheduled workflow (1/2) to invoke the Batch API (3) on a regular basis and then store the retrieved CSV in Retool Storage (4).
- Select Retool Home > Workflows > Create new > Workflow
- Rename the workflow
csv-batch-api.
startTrigger block
The default workflow will include a startTrigger block, used to identify a schedule, webhook, or event, and a Code block. Delete the code block by selecting the ... > Delete. This will leave the startTrigger on its own. For this lab we will not configure the startTrigger and will run it manually.
getCSV block
Next we create a Resource Query block to call the API to retrieve the CSV result. In this example the CSV will be a simulated course enrollment and is available at the following endpoint.
- Select + > Resource query
- Update the endpoint to the following value
https://ojmu6fw0n8.execute-api.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/default/batchService
- Verify that the query works by selecting the play symbol. A response similar to below should display.
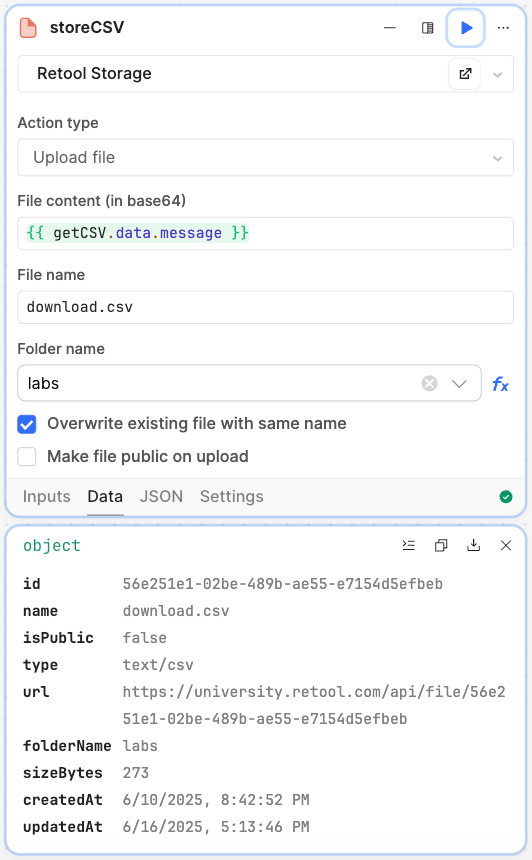
storeCSV block
Next we want to store the CSV file in Retool Storage so that a follow up process can extract, transform, and load the data into Retool Database.
-
Select + > Resource query
-
Change the name of the block to
storeCSVand specify the following settings:- Update the settings to use
Retool Storage - Action type to
Upload a file - File content is set to
{{ getCSV.data.message }} - File name is set to
download.csv - Folder name is set to
labs Overwrite existing file with same nameis checked
- Update the settings to use
-
Verify that the query works by selecting the play symbol. A response similar to below should display.
- Confirm a file called
download.csvis stored under thelabsfolder in Retool Storage.- Select Resources > Retool Storage > labs (folder).
- Confirm
downloads.csvexists.
invokeCSVToDB block
This step will invoke a workflow that hasn't been built yet. We will stub the block out and complete it later in the lab.
- Select + > Workflow
- Update the name of the block to
invokeCSVToDB.
Create csv-to-db workflow
This step will trigger a workflow to pull the CSV from Retool Storage (5) and upload the CSV content into rows in Retool Database (6).
- Select Retool Home > Workflows > Create new > Workflow
- Rename the workflow
csv-to-db.
This workflow will require that a Retool Database table exist in order to store the CSV contents.
Create table in Retool Database
First let's create the table in Retool Database to store the result of the csv-to-db workflow.
- Select Retool Home > Retool Database > + > Create table.
- Specify a table name of
etl_table. - Add the following fields and data types:
course_nameof typeTextstatusof typeTexttotal_enrolledof typeNumbertotal_completedof typeNumbercompletion_rateof typeNumbertime_spentof typeNumber
Develop csv-to-db Workflow
The following steps can be created using either JavaScript/Functions or Python.
- JavaScript
- Python
startTrigger block
In this block we will add some test inputs as shown in the following:
{
"folderName":"123",
"fileName": "123",
"url":"123"
}
getCSV block
Using the url parameter from the startTrigger, we can retrieve the contents of the file.
- Select + > Resource query
- Change the name of the block to
getCSV. - Specify the following values:
Retool Storage- Action type of
Get contents of file - Select
Fxand value of{{ startTrigger.data.url }}
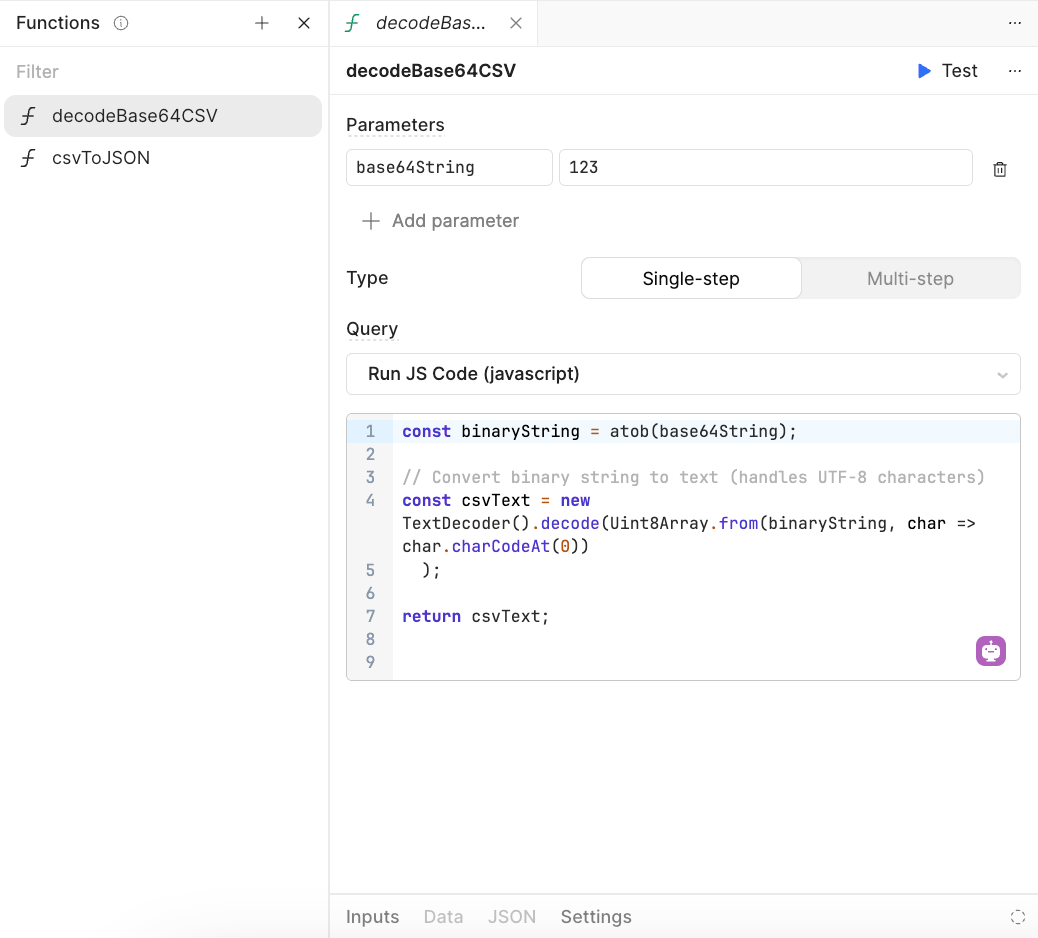
decodeCSV block
Next we want to convert the base64-encoded CSV file into text. Since this could be used by another workflow, we will create a function to perform this action.
- Select Functions.
- Update the name to
decodeBase64CSV. - Under Parameters > + Add parameter specify
base64Stringand a value of123. - Specify Type as Single-step.
- Specify Query as Run JS Code (javascript)
- In the code canvas cut and paste the following:
const binaryString = atob(base64String);
// Convert binary string to text (handles UTF-8 characters)
const csvText = new TextDecoder().decode(Uint8Array.from(binaryString, char => char.charCodeAt(0))
);
return csvText;
It will appear as the following in the function editor.
To leverage the function, we use a Code block configured with the following code:
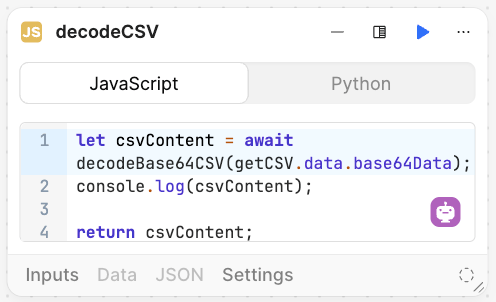
convertToJSON block
In order to store the CSV file we need to convert it from string into a JSON Array object. Using the comma separator value (,) and carriage return characters (/n) the following code creates a JSON Array object. JSON Array objects can be used to bulk insert into Retool Database.
To capture this logic we will use another single-step function.
- Select Functions.
- Update the name to
csvToJSON. - Under Parameters > + Add parameter specify
decodedStringand a value of123\n456\n. - Specify Type as Single-step.
- Specify Query as Run JS Code (javascript)
- In the code canvas cut and paste the following:
// Split into lines and get headers
const lines = decodedString.split('\n');
const headers = lines[0].split(',').map(header => {
// Clean up header and convert to snake_case
const cleanHeader = header.replace(/^"(.*)"$/, '$1').trim();
return cleanHeader
.toLowerCase()
.replace(/[^\w\s]/g, '') // Remove special characters
.replace(/\s+/g, '_'); // Replace spaces with underscores
});
// Process data rows
const result = [];
for (let i = 1; i < lines.length; i++) {
if (!lines[i].trim()) continue; // Skip empty lines
// Handle quoted values with commas inside them
const row = {};
let currentPosition = 0;
let fieldValue = '';
let inQuotes = false;
for (let j = 0; j < headers.length; j++) {
// Reset for new field
fieldValue = '';
// Process characters until we find a comma outside quotes or end of line
while (currentPosition < lines[i].length) {
const char = lines[i][currentPosition];
// Handle quotes
if (char === '"') {
inQuotes = !inQuotes;
currentPosition++;
continue;
}
// If we hit a comma outside quotes, we're done with this field
if (char === ',' && !inQuotes) {
currentPosition++;
break;
}
// Add character to field value
fieldValue += char;
currentPosition++;
}
// Add field to row object
row[headers[j]] = fieldValue;
}
result.push(row);
}
return result;
It will appear as the following in the function editor.
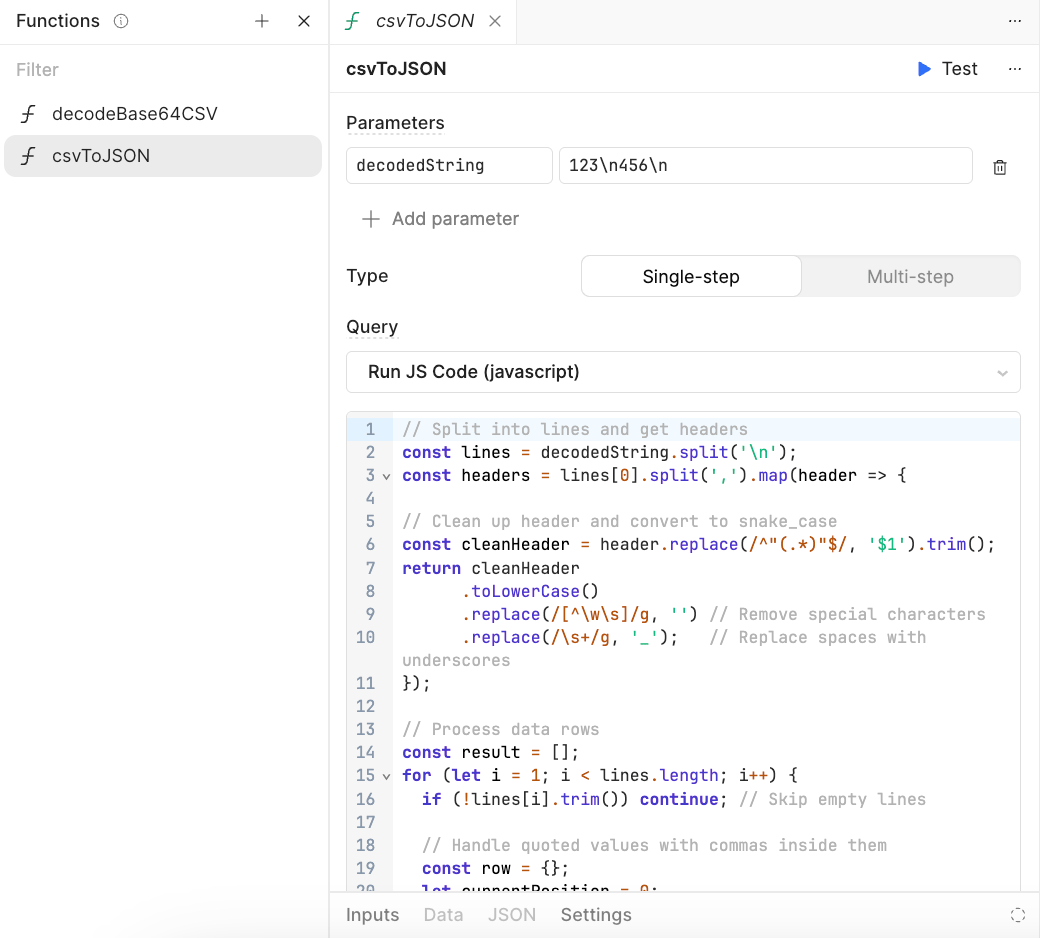
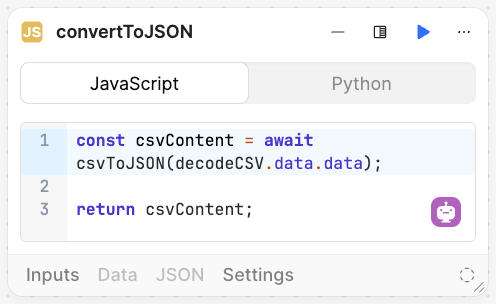
To leverage the function, we use a Code block configured with the following code:
const csvContent = await csvToJSON(decodeCSV.data.data);
return csvContent;
This will appears as shown in the following image.
truncateTable block
Before we store the data into a table, we want to truncate the table and reset the id. This will remove prior storage of the CSV and reset the table.
- Select + > Resource query
- Change the name of the block to
truncateTable. - Specify the following SQL query:
TRUNCATE TABLE etl_table RESTART IDENTITY;
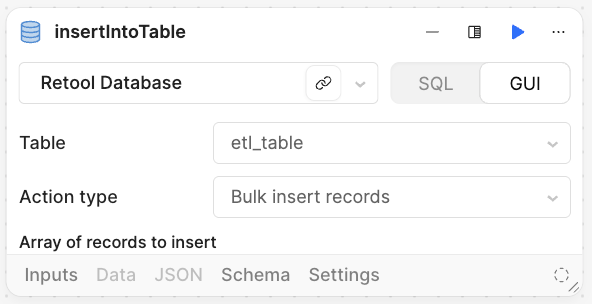
insertIntoTable block
The final step is to now store the JSON Array into Retool Database.
- Select + > Resource query
- Change the name of the block to
insertIntoTable. - Select
GUI. - Specify the following values:
- Table is set to
etl_table - Action type is set to
Batch insert
- Table is set to
Workflows has limitations with Python, specifically functions. We will use code blocks to perform these activities.
startTrigger block
In this block we will add some test inputs as shown in the following:
{
"folderName":"123",
"fileName": "123",
"url":"123"
}
get_csv block
Using the url parameter from the startTrigger, we can retrieve the contents of the file.
- Select + > Resource query
- Change the name of the block to
get_csv. - Specify the following values:
Retool Storage- Action type of
Get contents of file - Select
Fxand value of{{ startTrigger.data.url }}
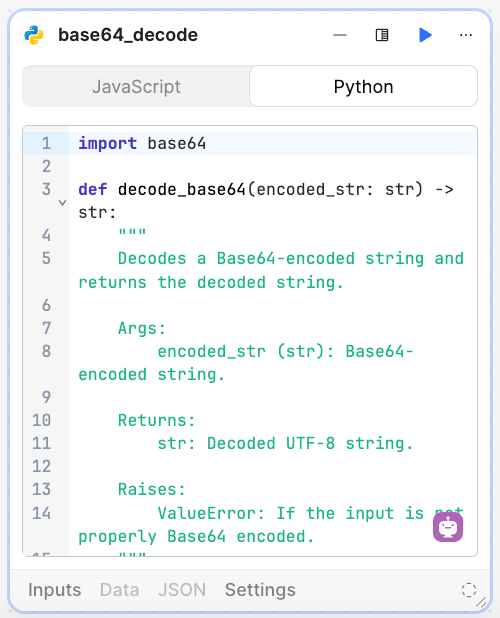
base64_decode block
Next we want to convert the base64-encoded CSV file into text. We use a Code block set to Python and paste the following code in.
import base64
def decode_base64(encoded_str: str) -> str:
"""
Decodes a Base64-encoded string and returns the decoded string.
Args:
encoded_str (str): Base64-encoded string.
Returns:
str: Decoded UTF-8 string.
Raises:
ValueError: If the input is not properly Base64 encoded.
"""
try:
decoded_bytes = base64.b64decode(encoded_str)
return decoded_bytes.decode('utf-8')
except Exception as e:
raise ValueError(f"Invalid Base64 input: {e}")
decoded = decode_base64(get_csv.data.base64Data)
return decoded
The following image shows the completed block.
convert_to_json block
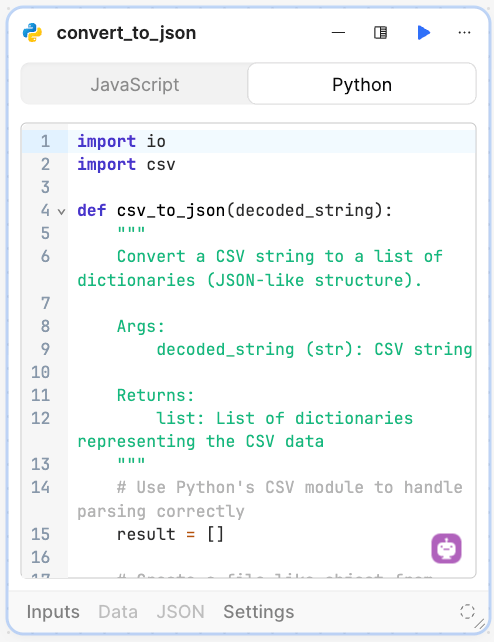
In order to store the CSV file we need to convert it from plain text into a JSON Array object. We use a Code block set to Python and paste the following code in.
import io
import csv
def csv_to_json(decoded_string):
"""
Convert a CSV string to a list of dictionaries (JSON-like structure).
Args:
decoded_string (str): CSV string
Returns:
list: List of dictionaries representing the CSV data
"""
# Use Python's CSV module to handle parsing correctly
result = []
# Create a file-like object from the string
csv_file = io.StringIO(decoded_string)
# Read the CSV file
csv_reader = csv.reader(csv_file)
# Get headers from first row
headers = next(csv_reader)
# Clean up headers and convert to snake_case
clean_headers = []
for header in headers:
# Remove quotes if present and trim whitespace
clean_header = header.strip()
if clean_header.startswith('"') and clean_header.endswith('"'):
clean_header = clean_header[1:-1]
# Convert to snake_case
clean_header = clean_header.lower()
clean_header = ''.join(c for c in clean_header if c.isalnum() or c.isspace())
clean_header = clean_header.replace(' ', '_')
clean_headers.append(clean_header)
# Process data rows
for row in csv_reader:
if not any(row): # Skip empty lines
continue
# Create a dictionary for this row
row_dict = {}
for i, value in enumerate(row):
if i < len(clean_headers):
# Remove quotes if present
if value.startswith('"') and value.endswith('"'):
value = value[1:-1]
row_dict[clean_headers[i]] = value
result.append(row_dict)
return result
json = csv_to_json(base64_decode.data)
return json
The following image shows the completed block.
truncate_table block
Before we store the data into a table, we want to truncate the table and reset the id. This will remove prior storage of the CSV and reset the table.
- Select + > Resource query
- Change the name of the block to
truncate_table. - Specify the following SQL query:
TRUNCATE TABLE etl_table RESTART IDENTITY;
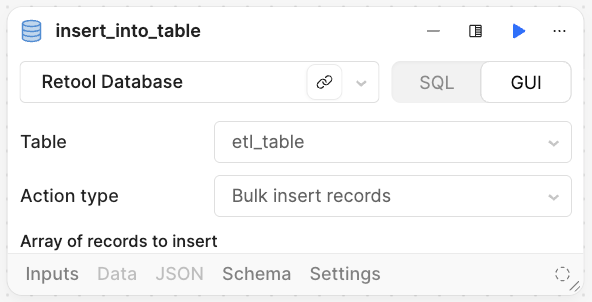
insert_into_table block
The final step is to now store the JSON Array into Retool Database.
- Select + > Resource query
- Change the name of the block to
insert_into_table. - Select
GUI. - Specify the following values:
- Table is set to
etl_table - Action type is set to
Batch insert
- Table is set to
Completed examples
You can import these completed examples to compare but it will require that you configure Retool storage and Retool database identified in the above steps.
- For both JS and Python examples: csv-batch-api
- JavaScript only: csv-to-db
- Python only: csv-to-db-python