Firebase query tutorial
Learn how to write queries directly against the Firebase Admin SDK in Retool.
Retool supports Firebase's Admin API and allows you to build CRUD apps on top of Firestore, RealtimeDB, and Auth data.
Working with Firestore
You need to connect a Firebase resource before you can work with Firestore. Follow the Connect to Firebase guide to connect a Firebase resource if you haven't yet.
Retool built a template that can help you get started with CRUD operations. To use the template, click Create new and then Create from template on your Retool homepage. Select the Firestore Admin Panel template to get started.
Query Firestore and get Collections
To query Firestore, create a new resource query and select Firestore from the Service type dropdown. Set the Action type to Query Firestore. You can also specify a collection using the dropdown, or input a custom value by clicking Use raw id.
Retool lets you query using a key (a document field), operators (==, in, >=, etc.), and a value. You can add as many statements as you need, and you can also set limits, order results by field, etc.
You can set the value of your key or value dynamically with JavaScript, which you can use to implement features like search. For example, you can use a Text Input component to pass a search term into the value input.
Format Firestore query results for a Table component
You can display the query's results in a Table component to view all the documents in a collection. Either select the query in the Data source dropdown, or use JavaScript ({{ query_name.data }}).
You may need to use lodash or other JavaScript libraries to reformat your data for display in the Table component. For example, use{{ _.values(query_name.data) }}, or for more advanced use cases, use .zipWith:
_.zipWith(_.keys(query_name.data), _.values(query_name.data), (key, value) => Object.assign({}, { key: key}, value))
You can write this code in the Data source field of the table, apply it as a transformer in your query, or create a transformer. See the transformer docs to learn more. You can also use helper functions, such as formatDataAsArray, but you might need to do some custom formatting.
Retool allows you to query available Firestore collections (top level or under a specific document ID), which you can use to dynamically select which documents to display in the table. To get started, create a query that lists top level collections.
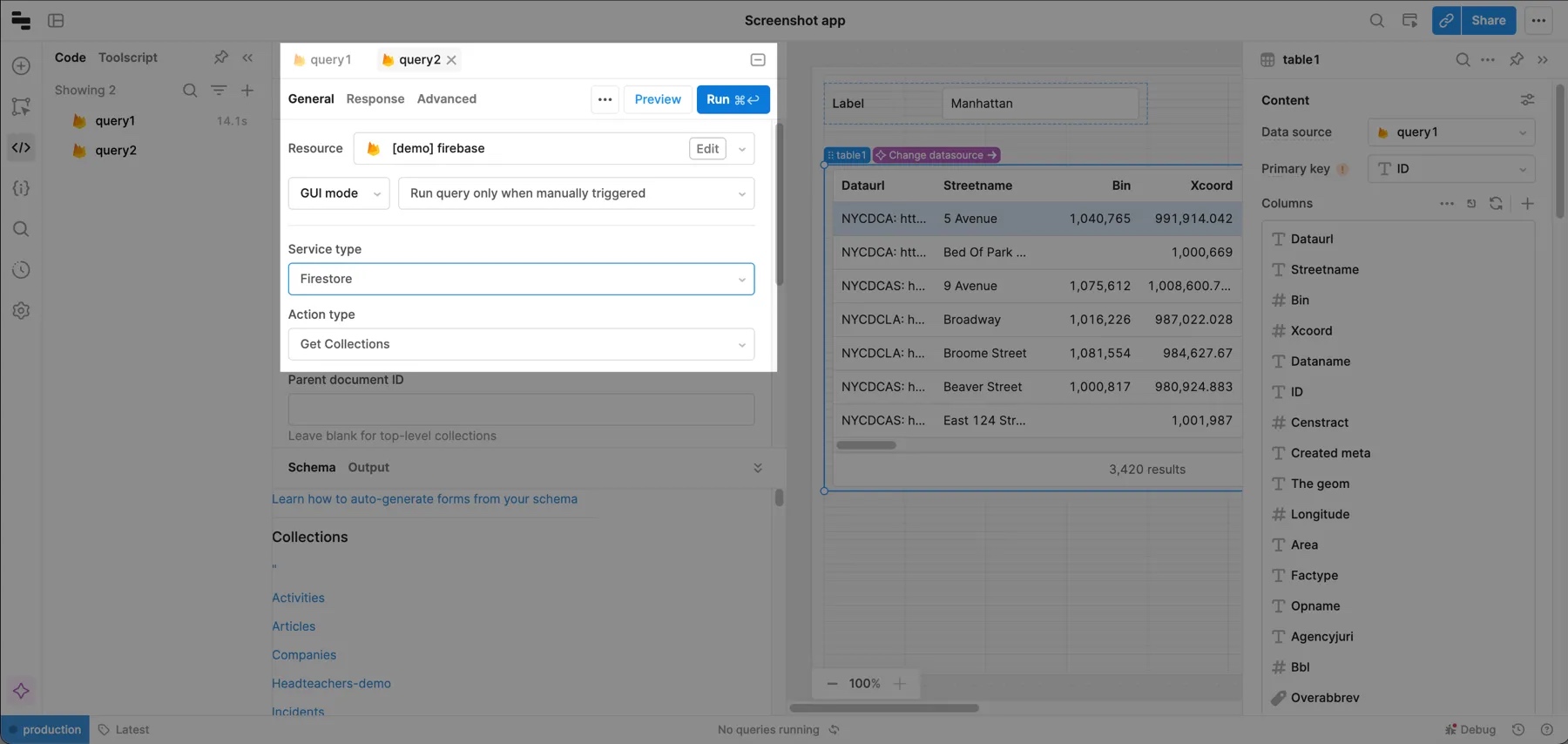
To query a nested collection, specify the Parent document ID. You can also specify the document path (e.g., home/locations/restaurants).
Next, display the results of this query in a Select component.
Then connect the value of the Select component to your original query (query1 in the example) by changing the Collection to use a raw ID and pass the value of the Select component. Make sure that your first query is set to run when inputs change.
Update documents in Firestore
To update a Firestore document, you need the document’s ID and the object to update it with. Create a new query, select your Firebase resource, choose Firestore from the Service type dropdown, and choose Update Document as the Action type.
Passing a partial object as the value updates only your passed fields.
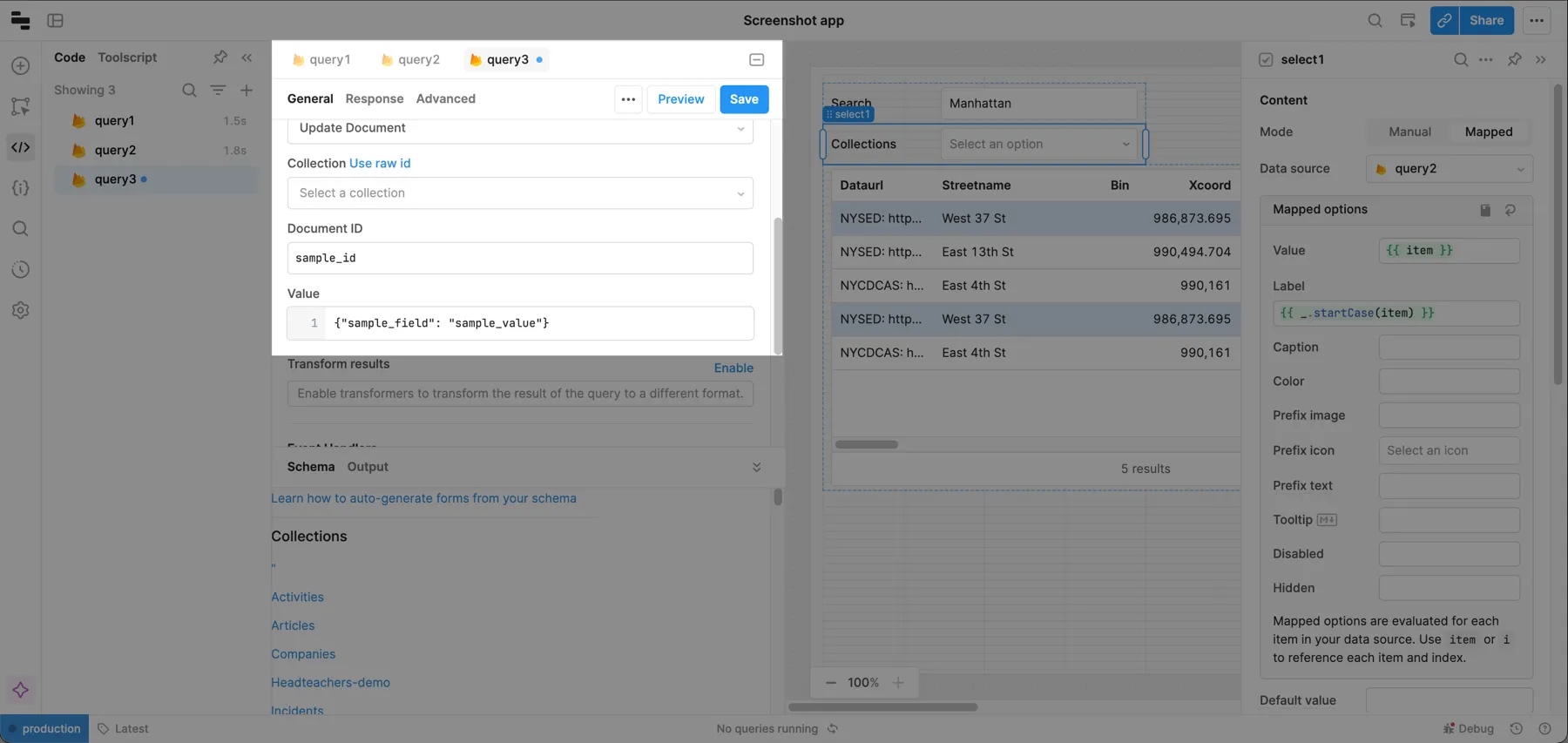
There are a few ways to build a UI for the update flow:
- Use a Form component with Text Input components for each document field you want to update.
- Use a JSON Editor component that lets you update values directly, and submit the changed values with a Button component.
- Make columns in the Table component editable.
You can choose whichever pattern fits your users’ needs, as long as you format the results as a JSON object and pass it in the Value field of your query. Both the document ID and value can be dynamic, so you can pass their values using JavaScript in {{ }}. For this guide, a Table component is used to make updates.
Select the table to make the columns editable. To simplify the example, a single column is made editable.
This makes the columns editable on the frontend but doesn't save the changes to your resource. To save the changes, open the query you created previously that updates a document.
For document ID, pass the ID of the edited row with {{ table1.changesetArray['0'].id }} (this works for updating a single row, but you'll learn how to update multiple rows in a subsequent section). Enable Use raw id for the collection, and pass the selected value from the dropdown.
When you edit tables, the changes are stored in the changesetArray property until they're saved. You can pass values from this property into queries. For this example, set the Value in the query to { "streetname": "{{ table1.changesetArray['0'].streetname }}"}. Your query should now look something like this.
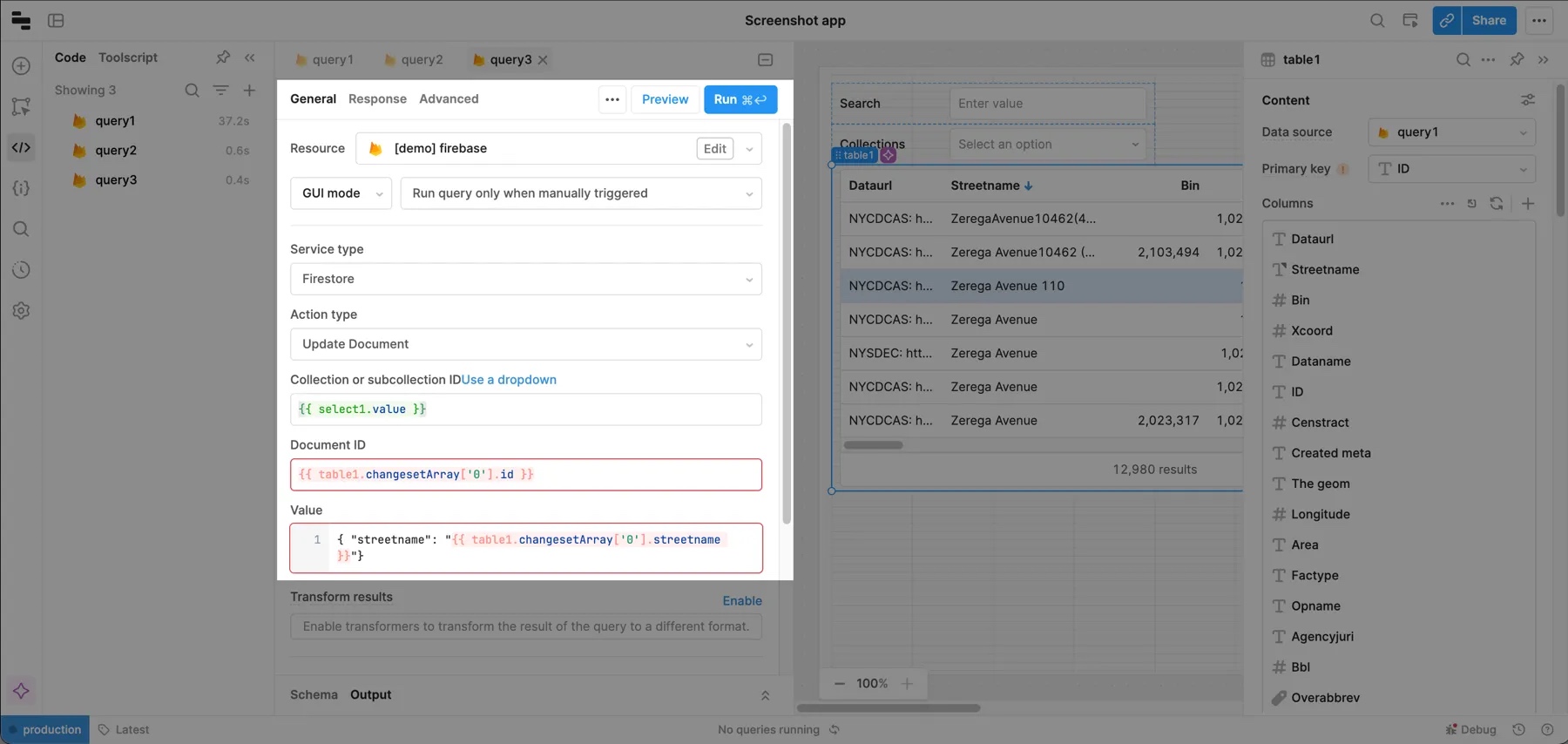
Make sure to save the query. If some of the values display an undefined error, this is expected if the table hasn't been edited yet.
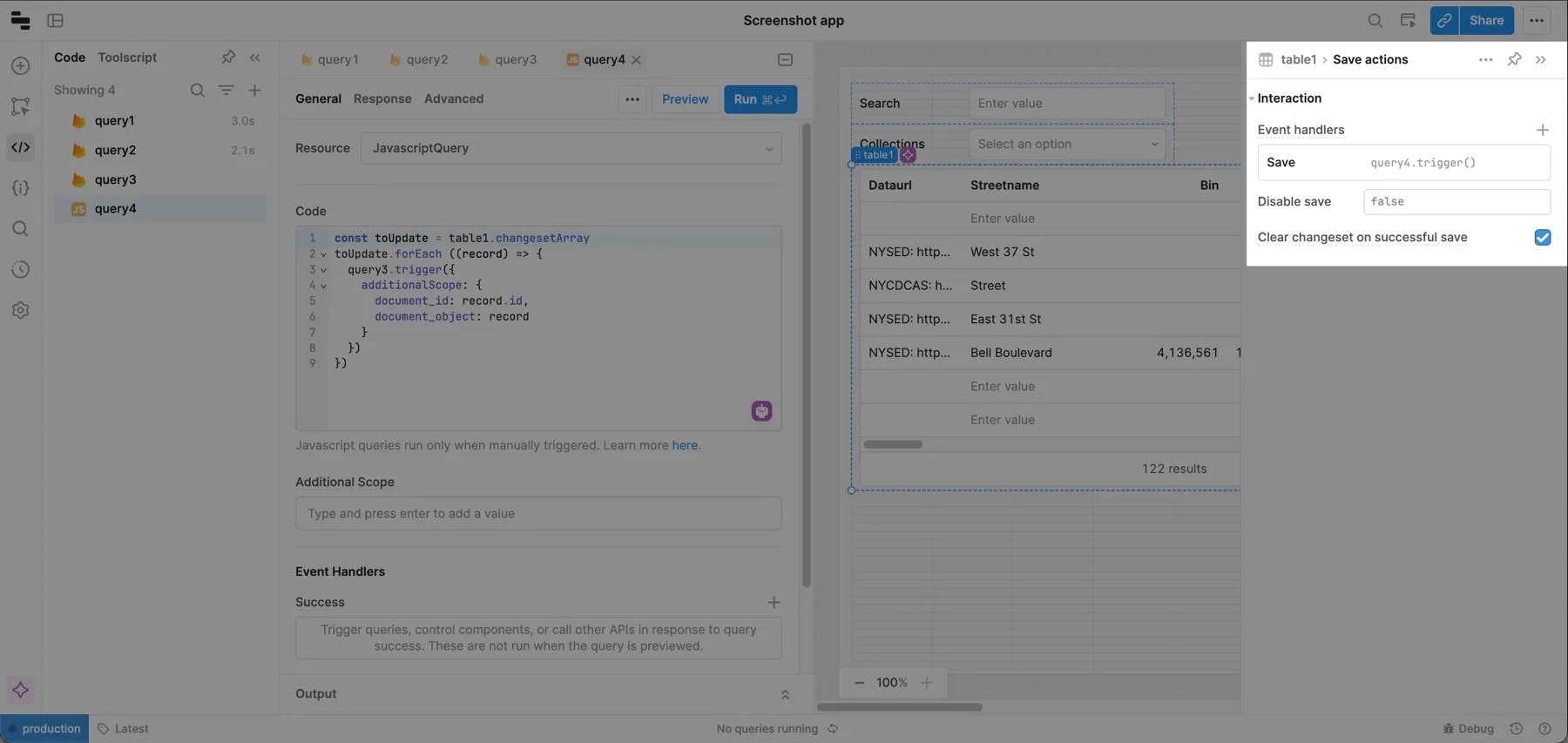
When a change is saved, the update query needs to run, but the table also needs to be refreshed after the update. To do this, add a Save action to the table, connect it to the update query, and then add a success event handler to the update query that triggers your original query. The demo below illustrates this process.
Edit the streetname for one of the rows and then click Save to test the workflow.
Update multiple rows
The app currently supports updating a single row. To update multiple rows, create a JavaScript query that iterates through the table's changesetArray property, which contains all the changes. On each iteration, you trigger the update query for the changed row.
const toUpdate = table1.changesetArray
toUpdate.forEach ((record) => {
query3.trigger({
additionalScope: {
document_id: record.id,
document_object: record
}
})
})
This code uses additionalScope to pass values from table1.changesetArray to query3, which updates each row.
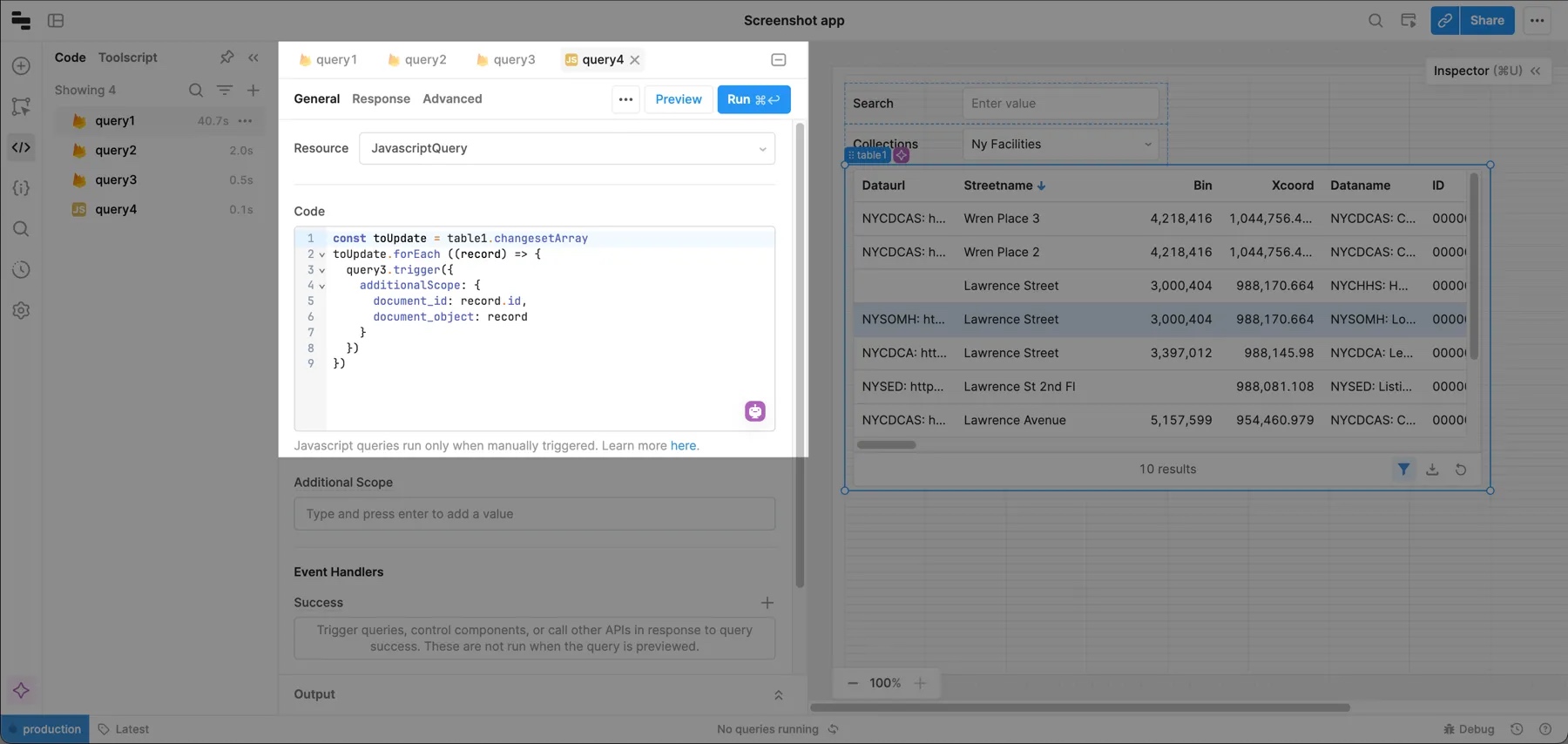
To connect your JavaScript to the update query, set the Document ID to {{ document_id }} and Value to {{ document_object }}. These values are passed from additionalScope.
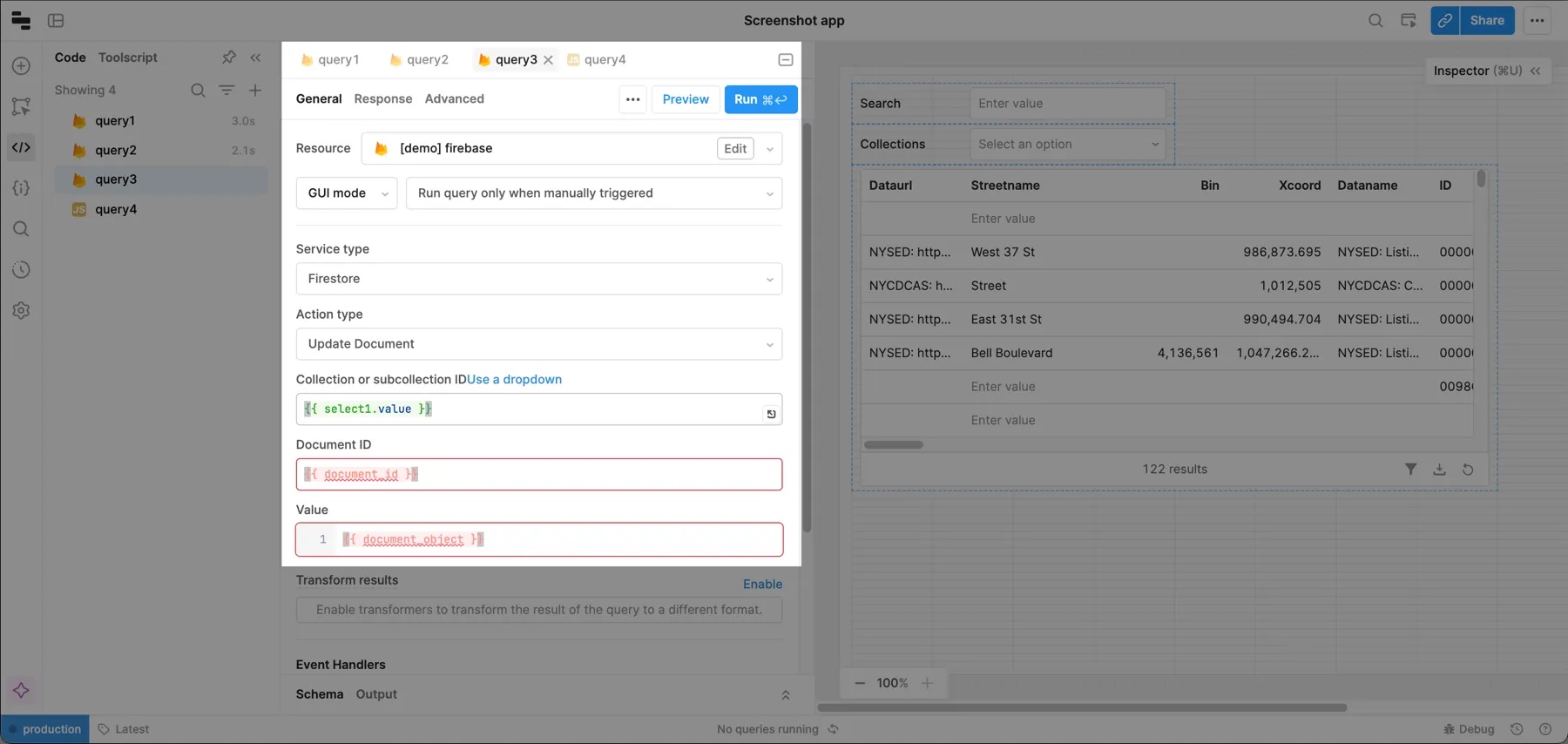
Finally, update the save action on the table to trigger the JavaScript query instead of the update query.
You can now edit multiple street names to test this functionality.
Use references in Firestore queries
If your Firestore query needs to use Database References, you can reference them in Retool using the $ref identifier in the value of your query.
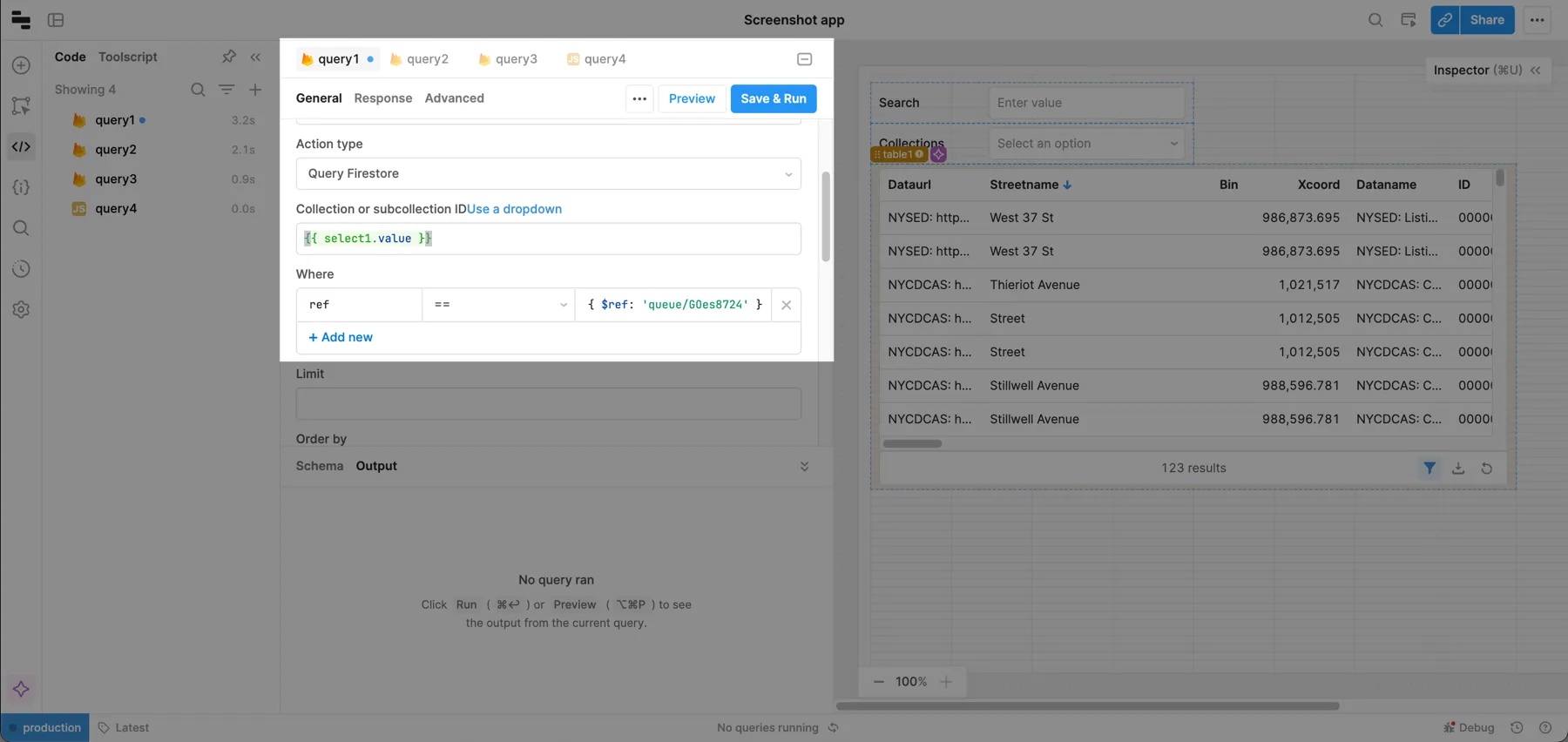
The syntax is similar to MongoDB Extended JSON syntax, where $ref specifies that the string should be a ref.
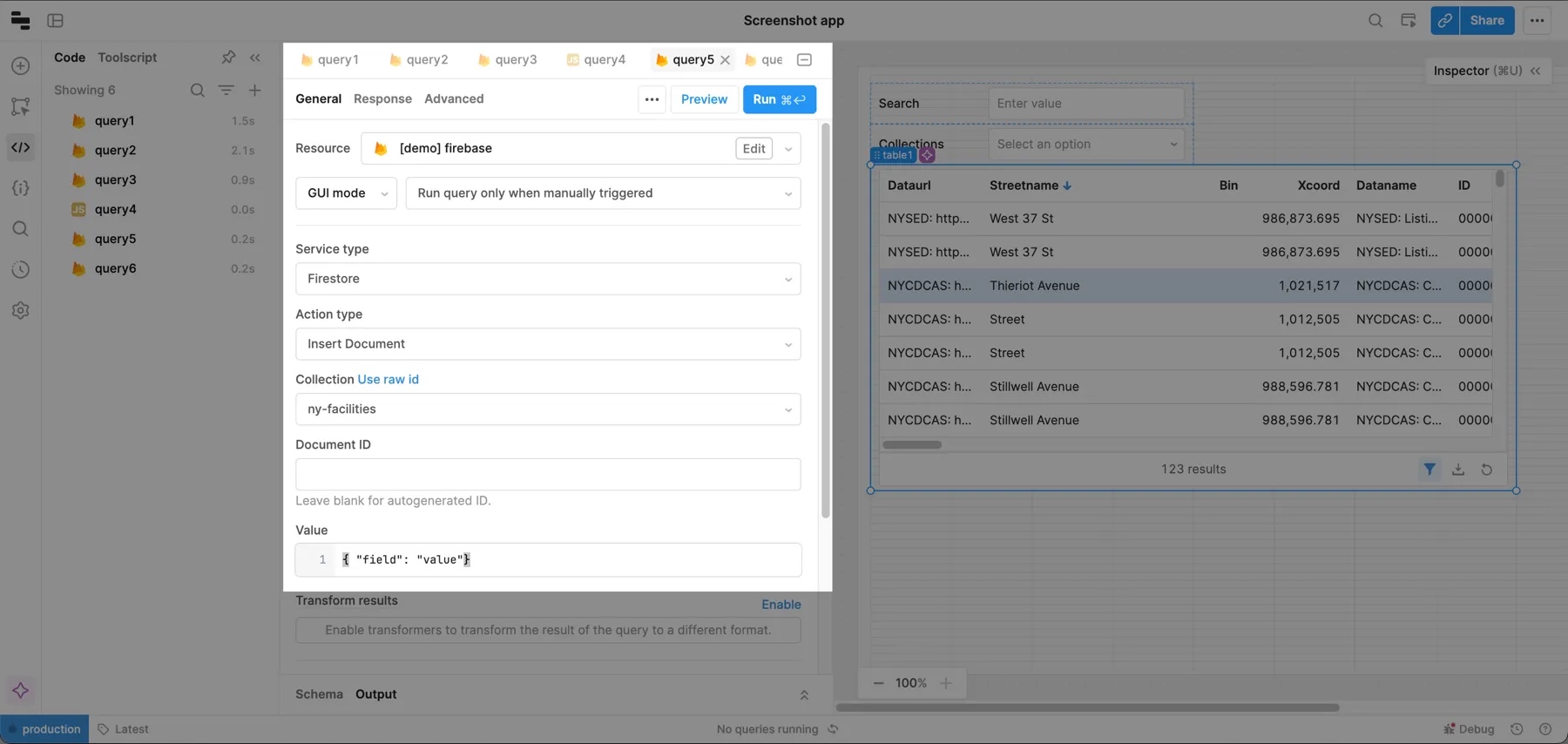
Insert a document
Create another query and select your Firebase resource. Then set:
- Service type to Firestore.
- Action type to Insert document.
- Your Collection value.
Inserting a document in Retool takes the same format as updating a document, but you can leave the document ID blank if you want Firestore to automatically generate one.
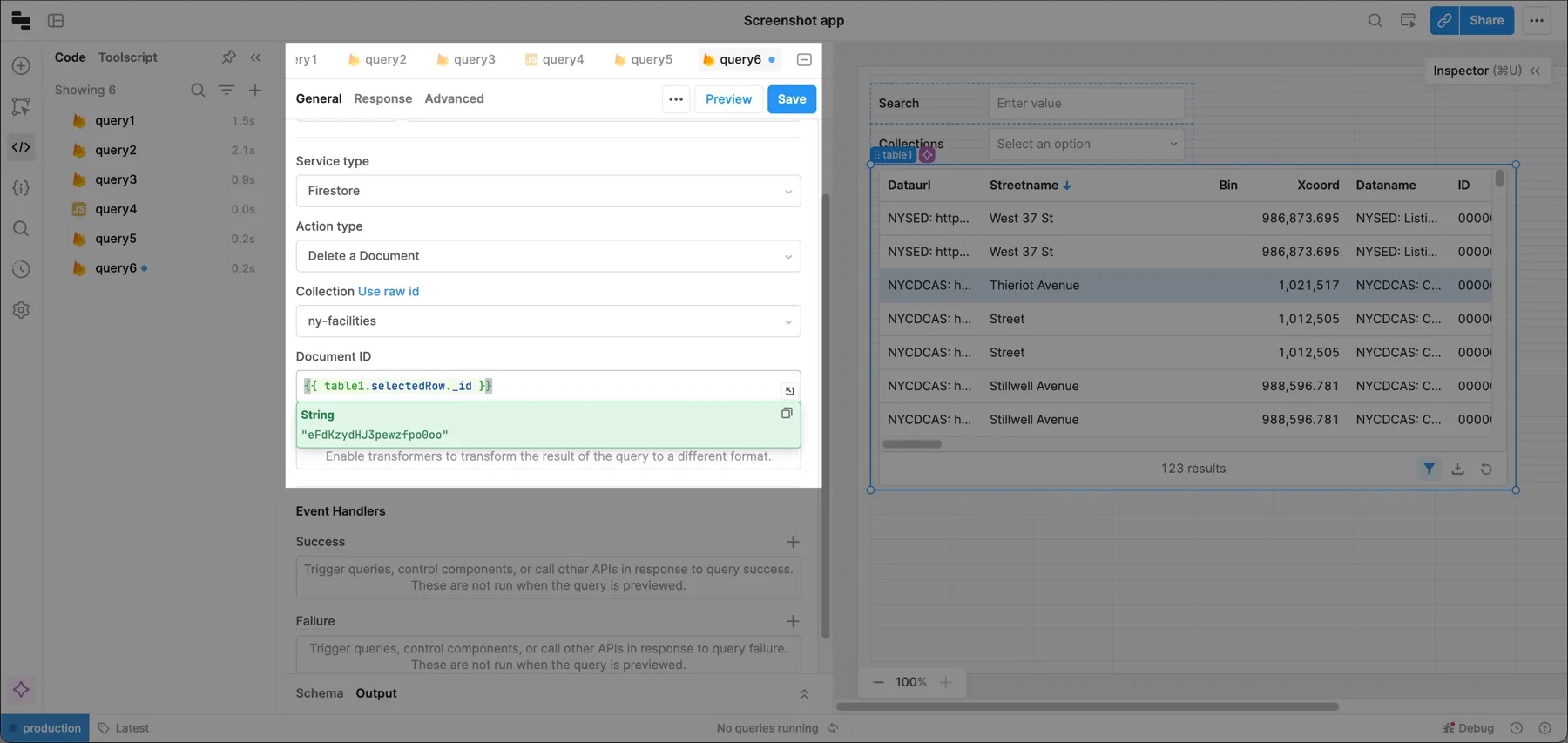
Delete a document
Create another query and select your Firebase resource. Then set:
- Service type to Firestore.
- Action type to Delete document.
- Your Collection value.
The only parameter you need to provide is a document ID, which you can pass dynamically based on the selected row (e.g., {{ table1.selectedRow._id }}).
Get document by ID
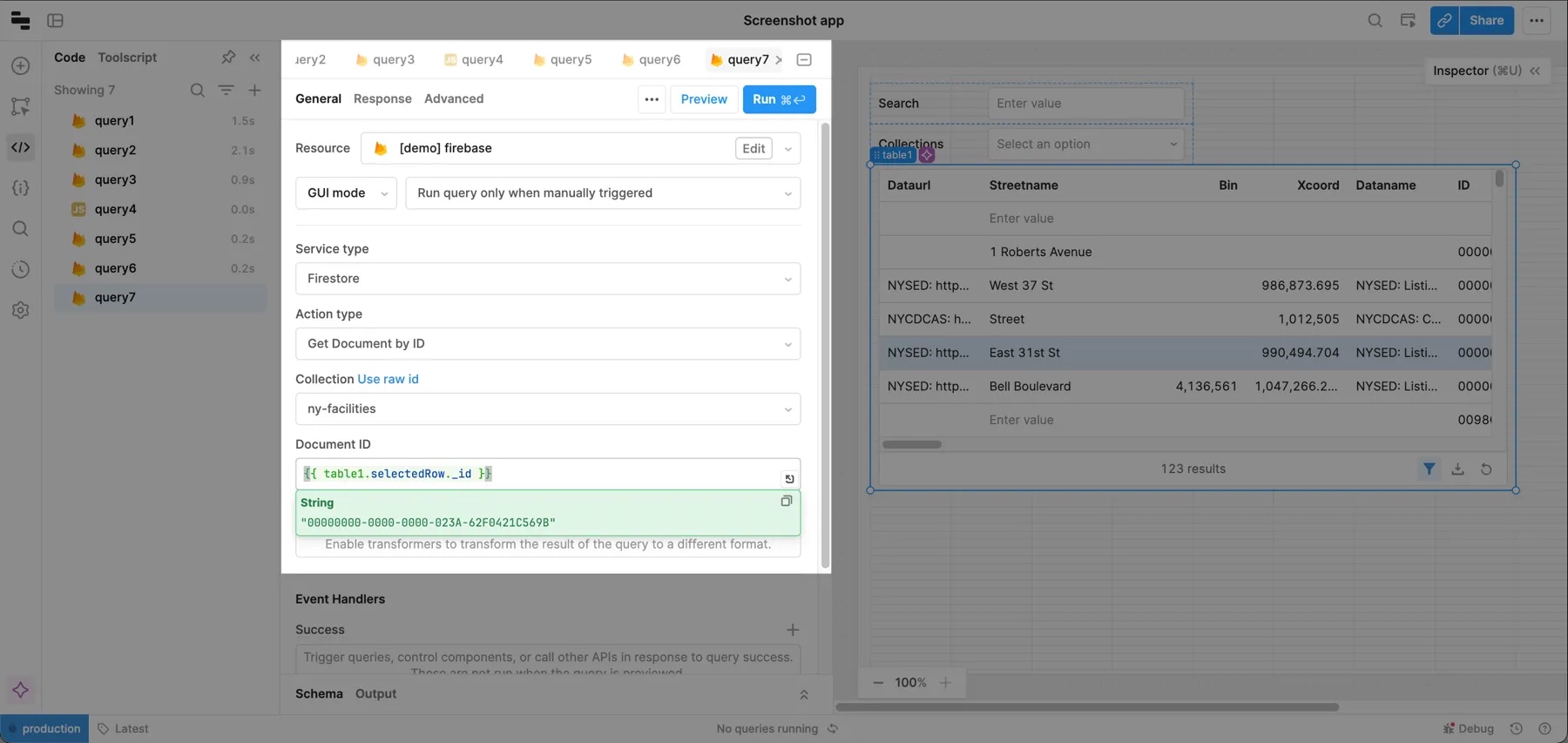
Create another query and select your Firebase resource. Then set:
- Service type to Firestore.
- Action type to Get Document by ID.
- Your Collection value.
The only parameter you need to provide is a document ID, which you can pass dynamically based on the selected row (e.g., {{ table1.selectedRow._id }}).
Working with RealtimeDB
Retool lets you get, update, and delete records in your RealtimeDB.
You must provide the Firebase database URL to query Firebase Realtime Database.
Query the database
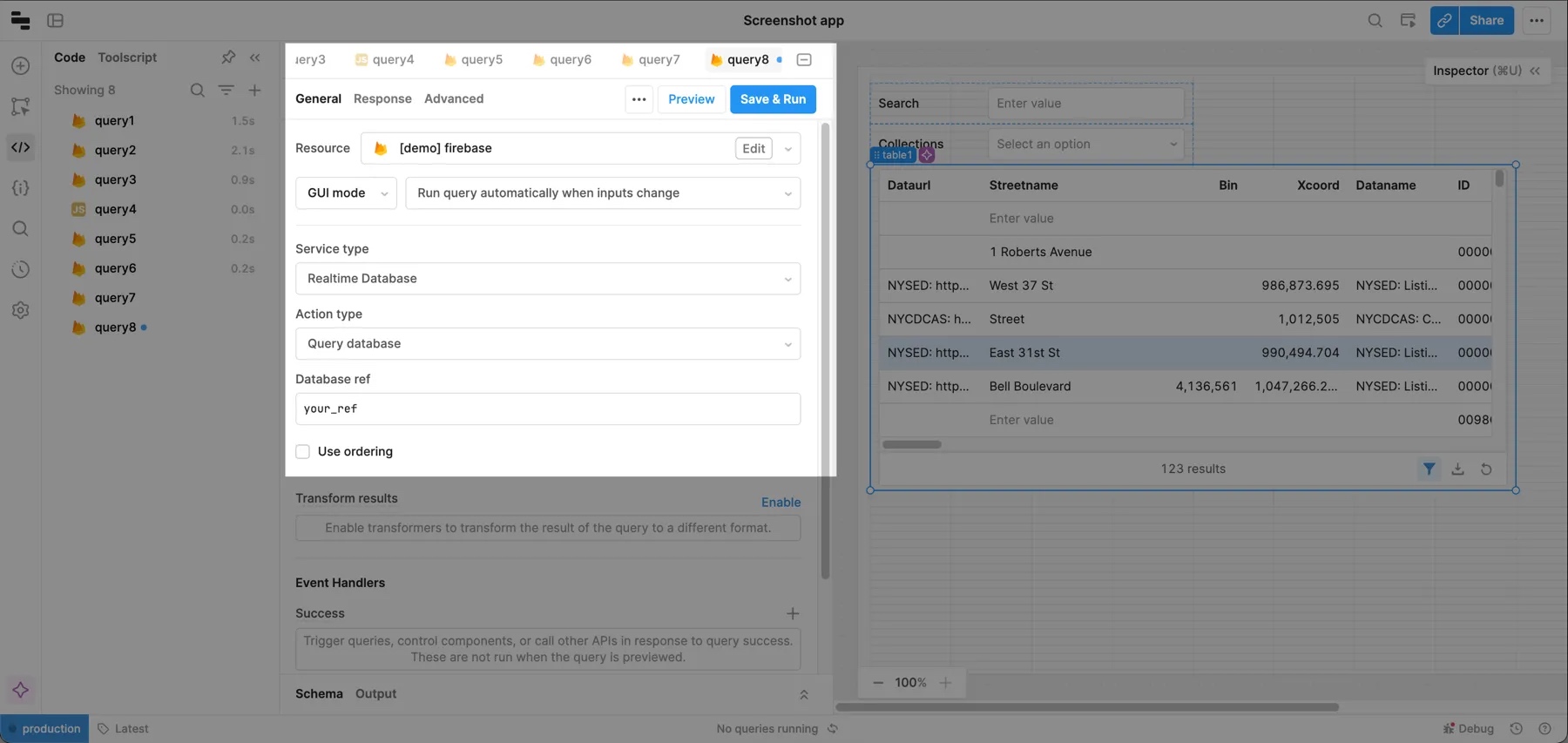
To query the RealtimeDB, create a query and select your Firebase resource. Then set:
- Service type to Realtime Database.
- Action type to Query Database.
- Your DatabaseReference.
If you enable Use ordering, you can access these ordering and filtering options.
- Order by child, key, or value.
- Limit to the first or last item.
- Use
equalTo,startAt, andendAtto filter your queries.
Set and update data
The Firebase database offers two APIs for updating data: .set() and .update().
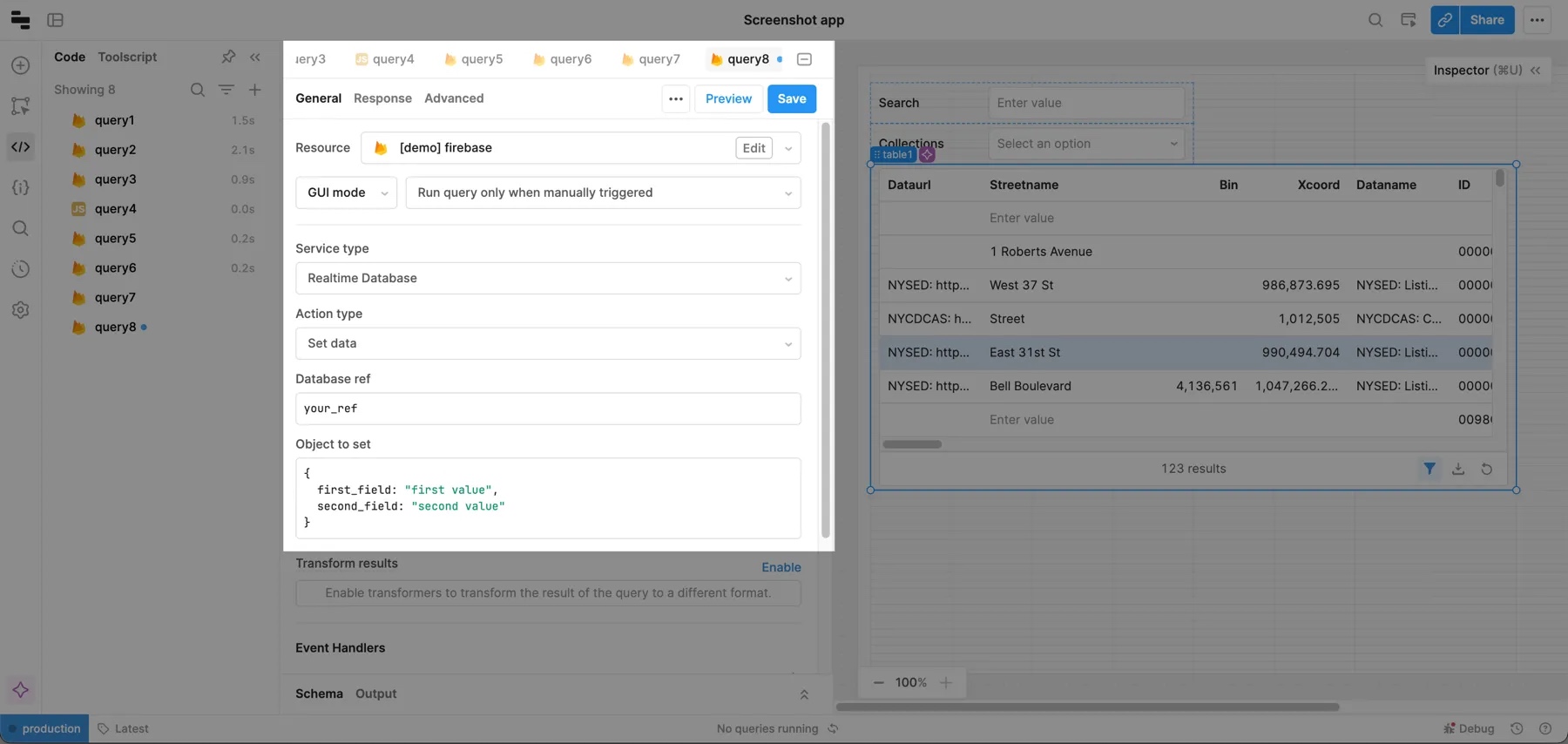
The .set() method replaces your chosen object with the value that you provide. For example, if your initial object has five fields, and you use .set() to only pass three fields, the updated object only contains the three fields. To use this method in Retool, choose Set from the Action type dropdown. You need to provide a database ref and an object to set.
The .update() method updates fields if they exist, but doesn't replace an entire object. The query format is the same as .set(), except that you set the Action type to Update data and provide your database ref and update object.
You can't run .update() or .set() queries on the root of your database. If your database ref doesn't have a / in it (e.g., references a child), your queries fail. If you input a database ref but the query still fails, you might need to try prepending it with a slash (e.g., /characters instead of characters).
Delete fields
Retool doesn't support deleting fields or objects directly, but you can use the set() method to change a value to null. When you .set() a property to null, it is deleted from the database. Make sure to pass null as JavaScript in curly braces, e.g., {{ null }}.
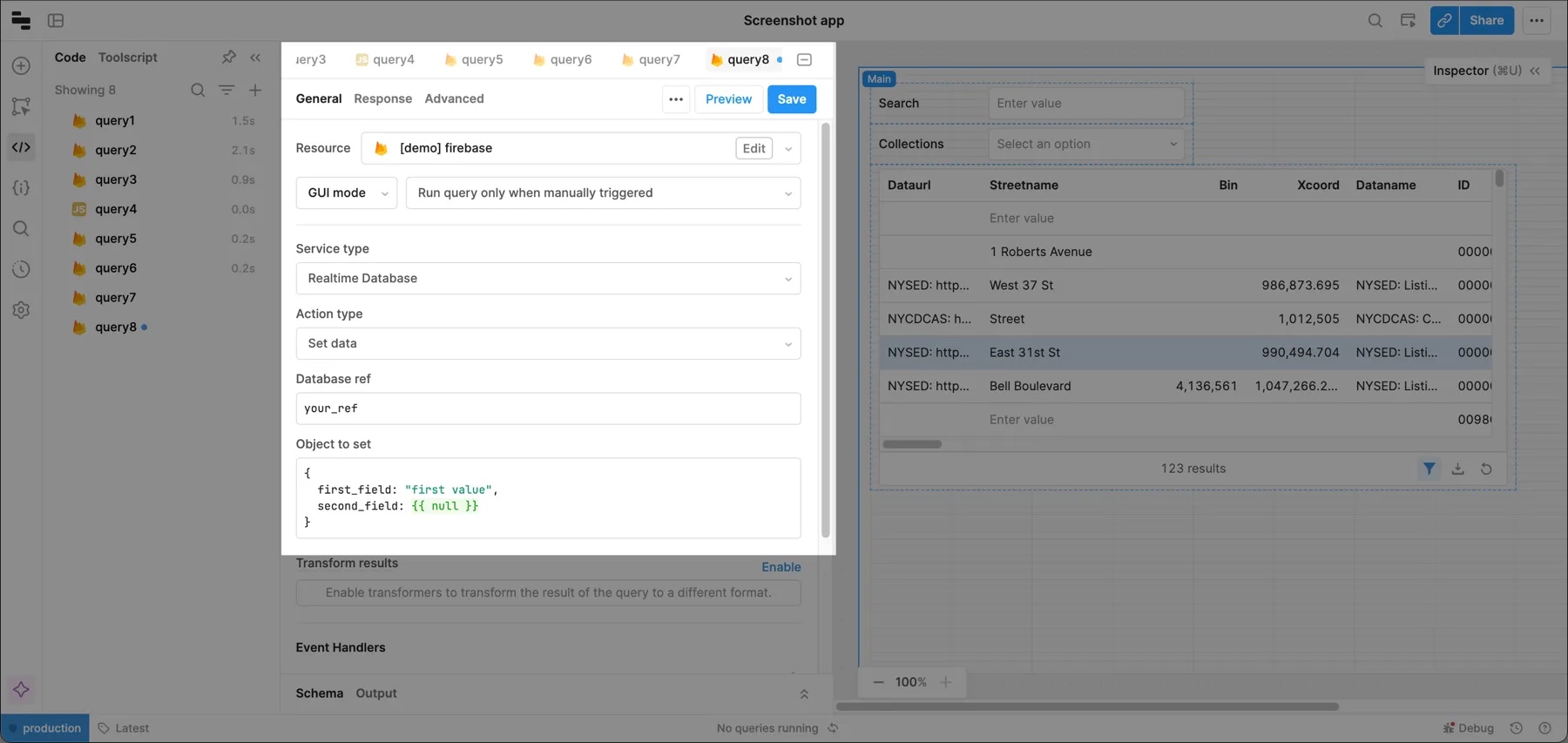
Working with Firebase Auth
Retool lets you view, update, add, and delete users from your Firebase Authentication setup.
If want to do basic CRUD operations on your Firebase Auth data, Retool built a template that can help you get started. See more details or click Create new and then Create from template on your Retool homepage. Look for the Firebase Auth Admin Panel template to get started.
List users
To list your existing Firebase Auth users, create a query and select your Firebase resource. Then set:
- Service type to Firebase Auth (user management).
- Action type to List users.
You can display the results of the query in a table by selecting the query as the table's Data source.
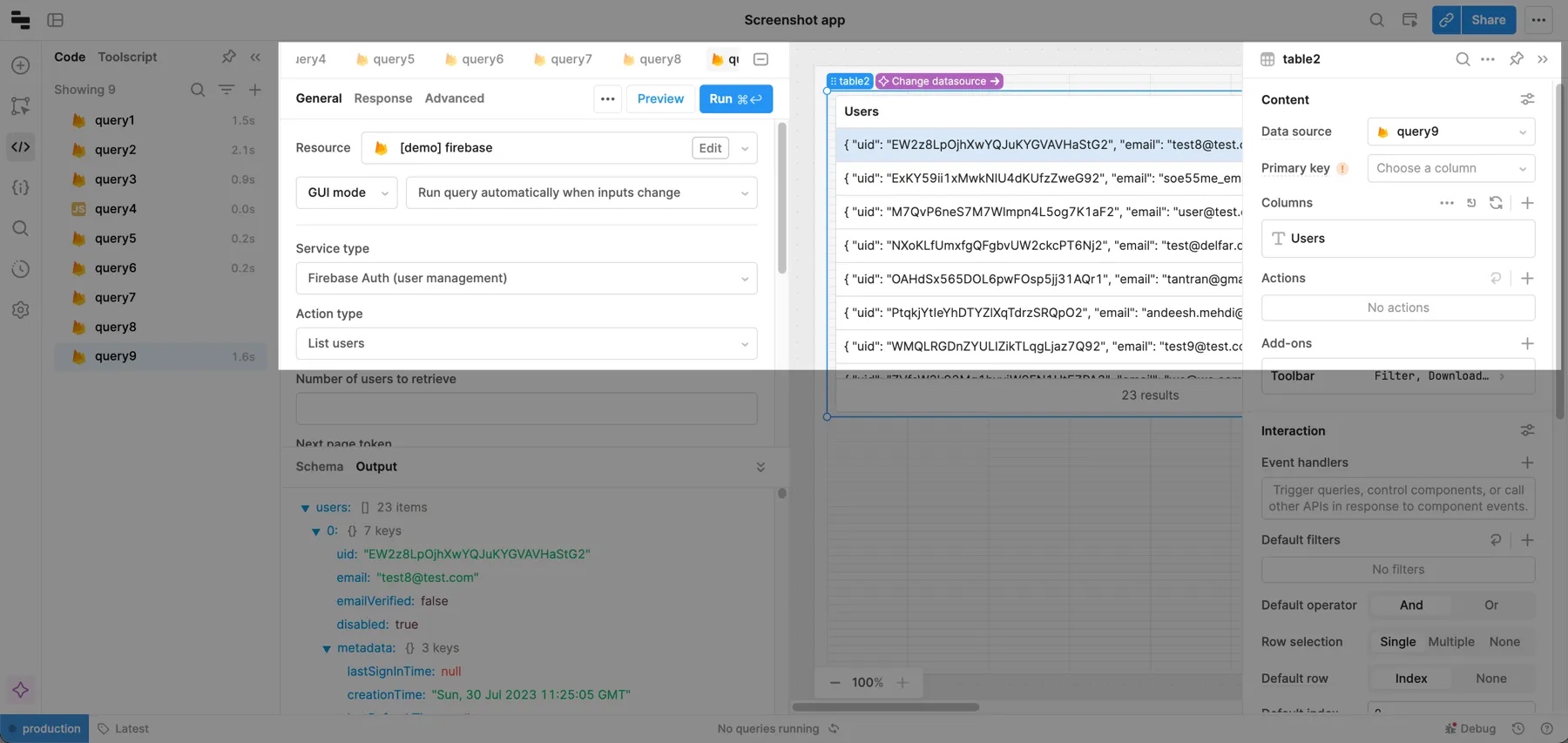
You can limit the number of users the query returns using the Number of users to retrieve property. You can set this value manually or use a dynamic value referencing a component's value—for example, {{ textInput1.value }}.
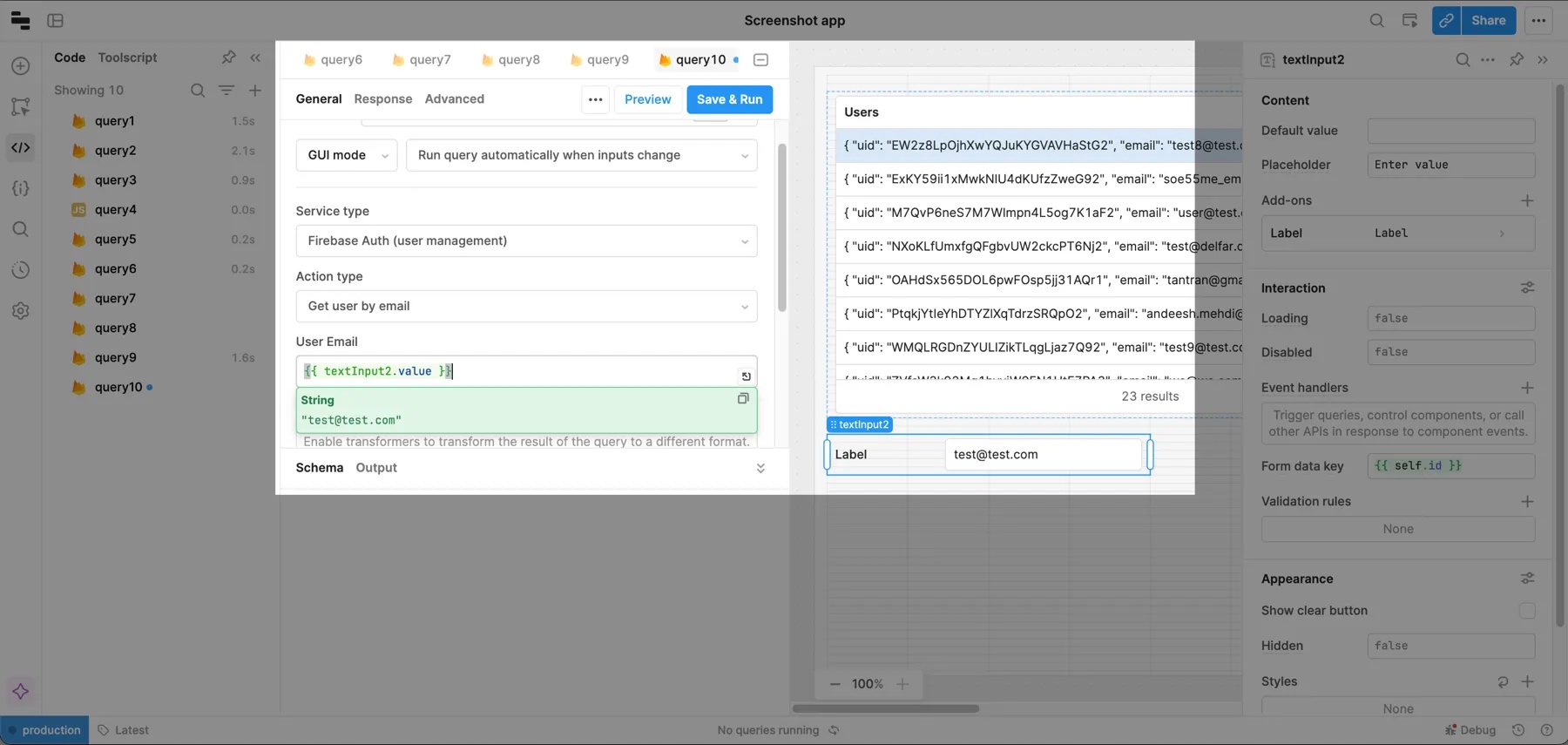
Get a user by UID, email, or phone number
To get a user by UID, email, or phone number, create a query and select your Firebase resource. Then set:
- Service type to Firebase Auth (user management).
- Action type to UID, email, or phone number.
The example query below retrieves a user by their email address, which is passed in dynamically from a Text Input component.
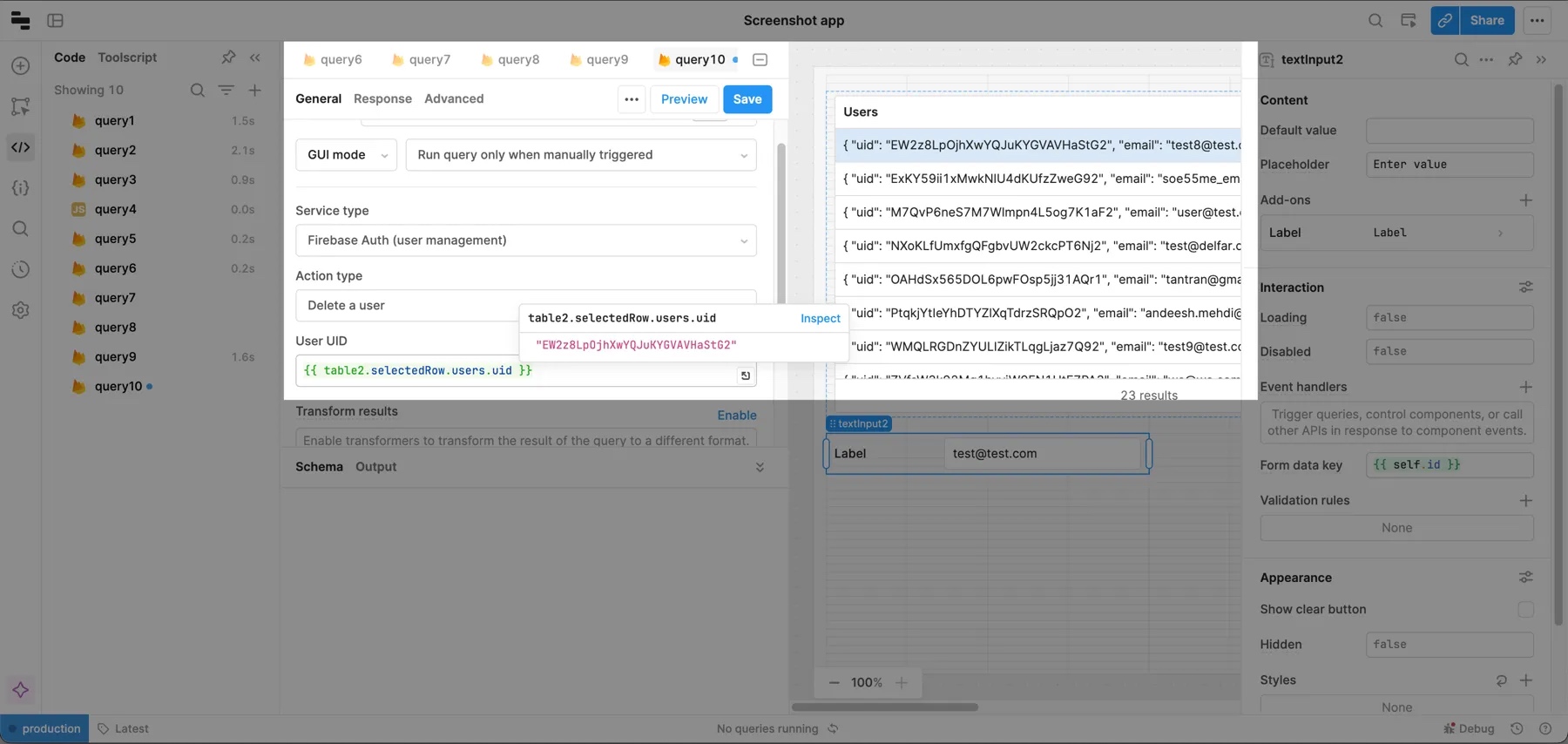
Delete a user
To delete a user, create a query and select your Firebase resource. Then set:
- Service type to Firebase Auth (user management).
- Action type to Delete a user.
You also need to pass the user's UID. In the example query below, the ID of the selected user is passed into the query.
Update a user’s information
To update a user’s information, create a query and select your Firebase resource. Then set:
- Service type to Firebase Auth (user management).
- Action type to Update a user.
You also need to pass the user's UUID and the update object.
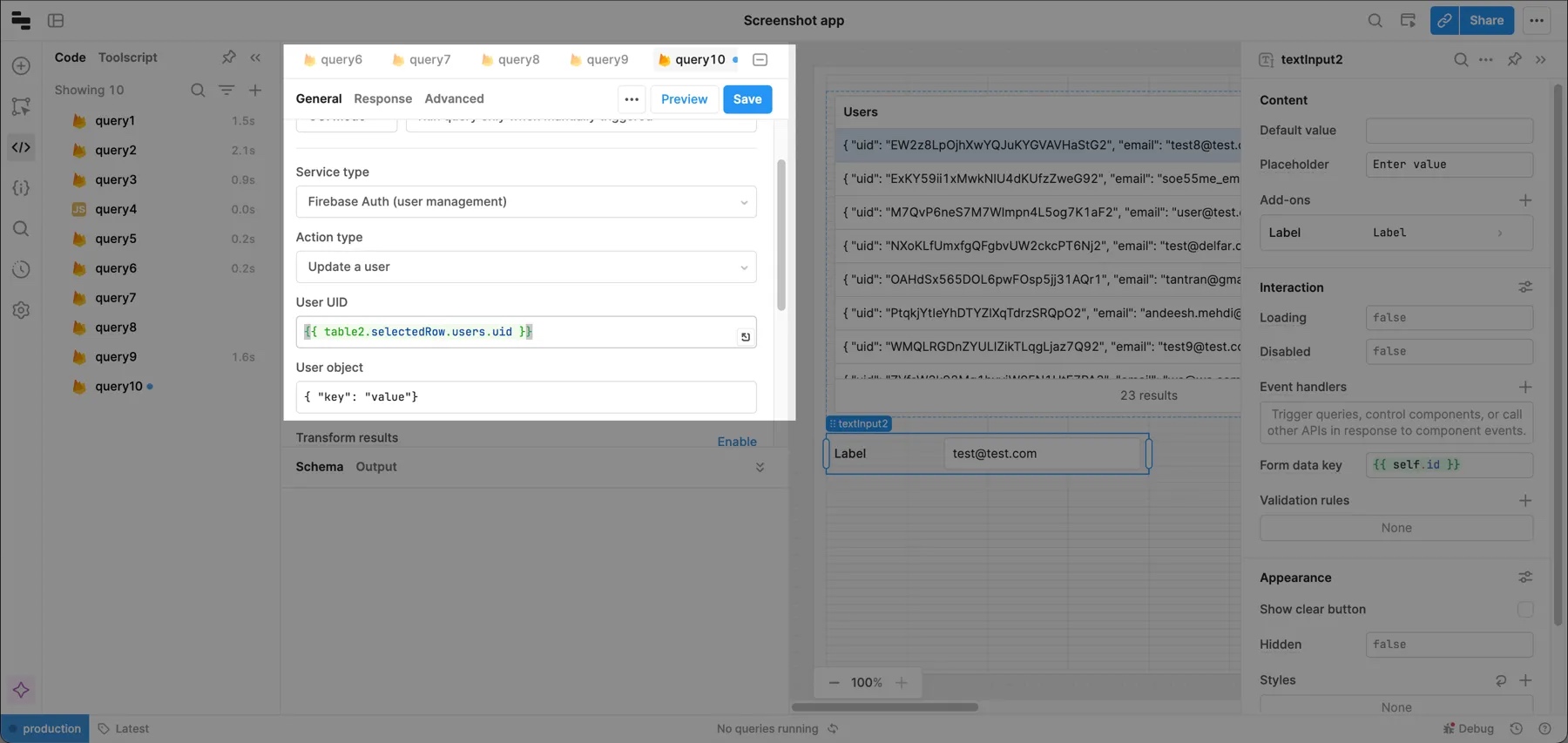
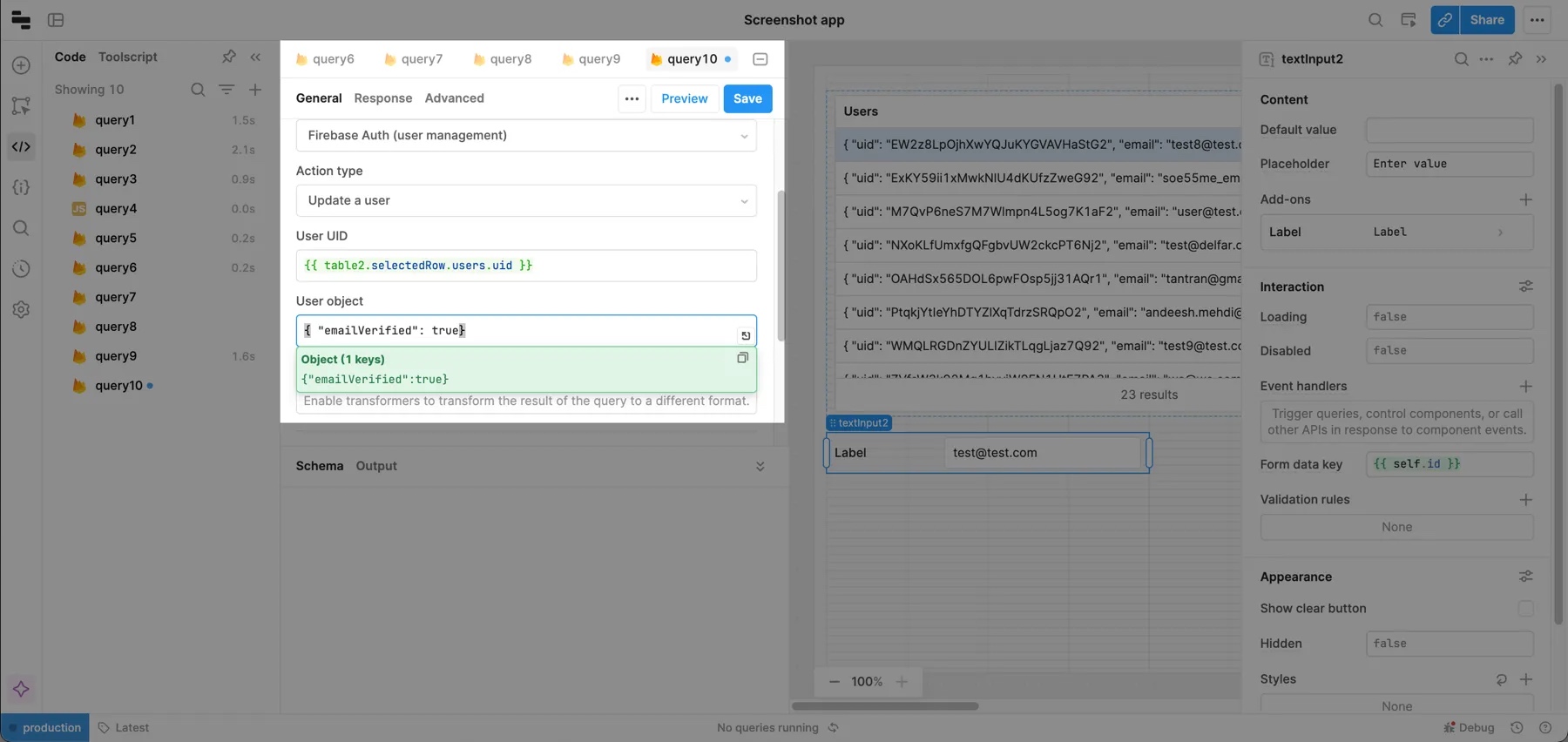
You can design your UI for updating users in various ways: a form, a raw JSON object, an editable table, etc. If you want to use a table, see the section above on updating documents for an example.
A common use case for Firebase Auth in Retool is verifying email addresses. You can use the update example for this.
Create a new user
To create a new user, create a query and select your Firebase resource. Then set:
- Service type to Firebase Auth (user management).
- Action type to Create a user.
You also need to provide a user object. Technically, the Firebase API doesn’t require you to include any fields, but Retool recommends passing at least an email address and password.
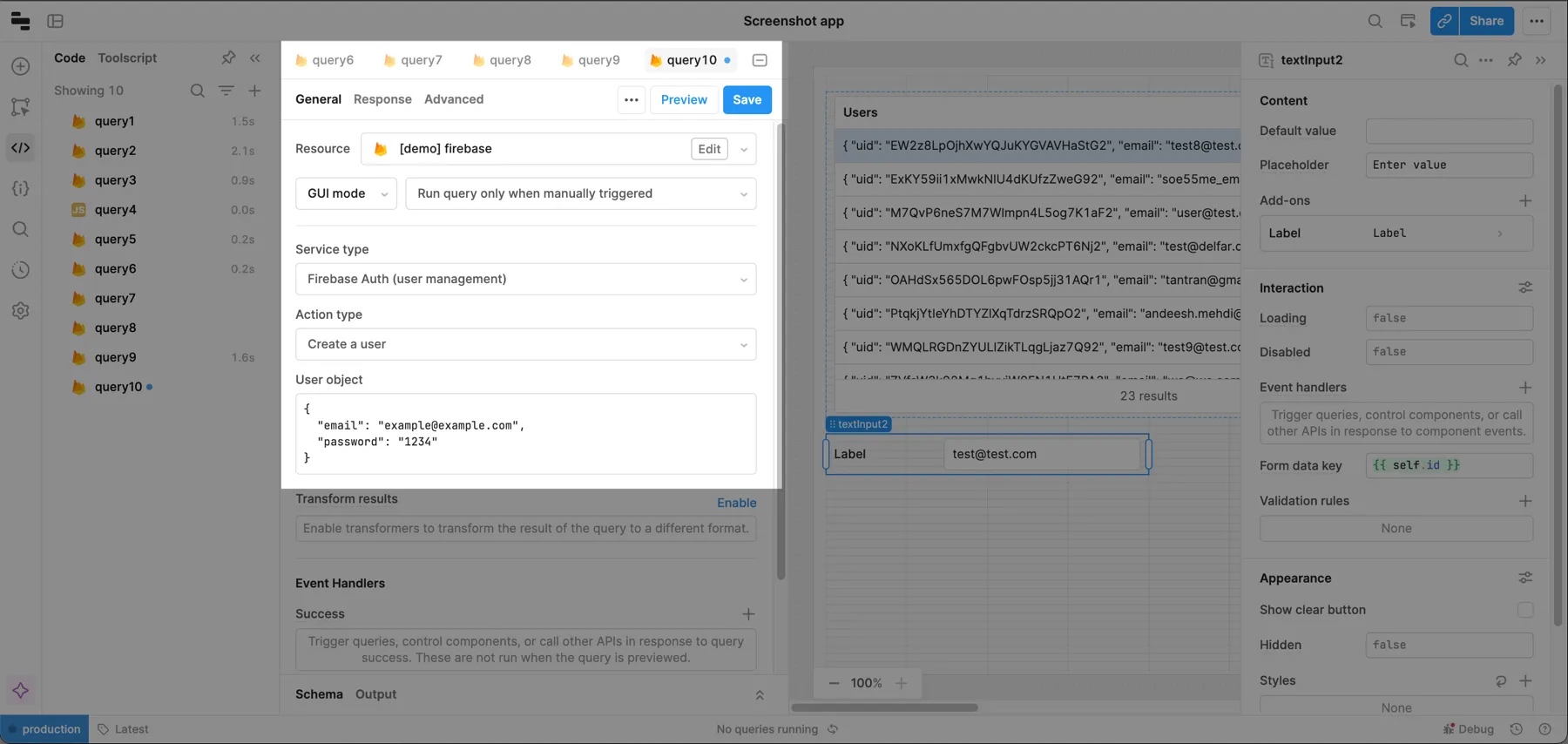
Remember that the user object field is dynamic, so you can pass values from other Retool components (a form, two text inputs, etc.) as you build your UI.
If you're running into any issues with Firebase/Firestore in Retool, check out some of the answered questions on our community forums, or ask one of your own.
Use timestamps in Firestore queries
Firestore uses a custom data type for timestamps and does not support string values. To write timestamps back to Firestore, provide the timestamp directly in a query, such as { lastUpdatedAt: {{ moment() }} } or { lastUpdatedAt: {{ new Date() }} }. Any values provided to a query using additionalScope are strings and cannot be used.