Retrieve secrets from HashiCorp Vault
Learn how to use HashiCorp Vault to store your Retool resource secrets.
| Secrets Manager Availability | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Self-hosted Edge 3.33 or later | Generally Available | ||
| Self-hosted Stable 3.33 or later | Generally Available | ||
Self-hosted Retool is available on an Enterprise plan only.
Configuring Resources in Retool can require handling sensitive values, e.g. database passwords or API keys. Retool is SOC 2 Type 2 compliant, and most customers store these values with Retool. However, depending on your security posture, you may want to store secret values externally, rather than encrypted in Retool’s database.
To support this, Retool supports retrieving secrets from HashiCorp Vault for customers running self-hosted Retool.
Requirements
Retool only supports versioned KV (v2) engines.
To use HashiCorp Vault with Retool, you need:
- A self-hosted Retool deployment
- A Retool organization on the Enterprise plan.
- Admin permissions for your Retool organization.
- Have HashiCorp Vault configured to store your secrets in a versioned KV (v2) engine.
1. Enable AppRole Auth Method
Follow the first two steps in the Vault tutorial to create a role for Retool with a policy to grant access to your secrets. The following is an example policy you might use.
path "secret-mount/data/*" {
capabilities = [ "read" ]
}
path "secret-mount/metadata/*" {
capabilities = [ "list" ]
}
Note: If your Vault instance supports namespaces, your AppRole policy must exist in the same namespace as your KV engine.
2. Get a RoleId and SecretId
Next, follow the third step from the Vault tutorial to get a RoleId and SecretId for the role created above.
3. Configure Secrets Manager in Retool
Secrets management must be configured for the primary organization, and for any spaces within an organization that need to use secrets.
For multiple deployment instances of Retool, make the same changes to your organization (and spaces within the organization) for each instance in which you want to use secrets.
For each Retool Space, visit Settings > Secrets Manager and enter the following settings from your Vault deployment.
| Setting | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Vault URL & Port | URL and port of your Vault server. | https://vault.mycorp.com:8200 |
| Path to KV Engine | The name of your KV engine. | secrets |
| Role ID | RoleId from Vault. | 40481de9-8281-cf4d-2056-abc5c738e392 |
| Secret ID | SecretId from Vault. | 12345d5a-ead6-5f9f-c683-a571ad716668 |
| AppRole Mount | Path at which the AppRole auth method is mounted. This defaults to approle/. | auth/approle |
| Vault Namespace | Full namespace path to the desired KV engine | ns1/ns2 |
Click Test connection to confirm Retool can connect to Vault, then click Save.
Retool Namespace
The Retool Namespace field is a value that will be prepended to any secret names Retool looks up. For example, if all your Retool-facing secrets in Vault start with retool/, you might set the namespace to be retool/ as well. If you have multiple Retool deployment instances, you can use this to resolve the same secret name in a Resource configuration to different secrets in Vault. For this reason, setting the namespace is recommended if you use Protected Resources.
For example, if you have "development" and "production" deployment instances, you might use the following naming convention for secrets in Vault:
// Secrets for development
retool/dev/db_user
retool/dev/db_password
// Secrets for production
retool/prod/db_user
retool/prod/db_password
On your Retool development instance, you would then set the namespace to retool/dev, and on your production instance to retool/prod. You can then reference secrets for either deployment instance using {{ secrets.db_user }} and {{ secrets.db_password }}, and Retool will fetch the appropriate secret at runtime.
Retool checks the validity of the configuration to ensure that secrets are available. If Retool cannot access the secrets manager you've configured, an error message appears in the Secrets Manager settings.
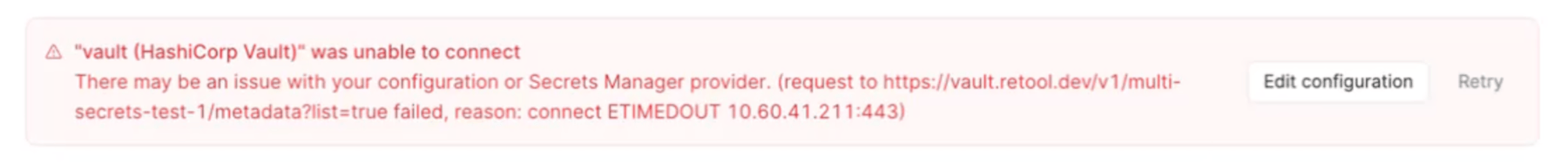
Validate secrets configuration.
4. Use secrets in resources
After you save your Secrets Manager configuration in Retool, if you granted Retool the read capability for the metadata, available secrets appear on Settings > Secrets Manager.
You can reference them in Resource configurations using template syntax, e.g. {{ secrets.name.key }} or {{ secrets['name'].key }}, either by copying values from the Reference column, or with autocomplete on the Resource configuration page.
You can access JSON keys with {{ secrets.name.key }} or {{ secrets['name']['key'] }}. You can access arbitrary levels of nested keys in your secrets. Note that keys will not autocomplete.
If your secret values are not quoted, you may need to wrap the template string in quotes in resource configurations.
For example, given an unquoted secret (secret-value) for the key key_name, you'd use "{{ secrets.key_name.key }}". Given a quoted secret ("secret-value"), you'd use {{ secrets.key_name.key }}.
When you rotate secrets in Vault, Retool automatically reads updated values from your secrets manager. This means you don't need to restart your Retool instance or update any configuration when rotating secrets.
Time to live (TTL) setting
Retool caches secrets it fetches with a configurable time to live. This reduces API calls to your secrets manager, which keeps queries fast and reduces costs. However, this means secrets may become temporarily "stale" when they are rotated. You can update Cache TTL (ms) in Settings > Secrets Manager to minimize failed queries in the event that a secret is rotated.
Security considerations
Any user that can configure resources can use secrets in resources. This could lead to inappropriate uses of secrets. You can restrict the list capability in Vault to mitigate the risk.