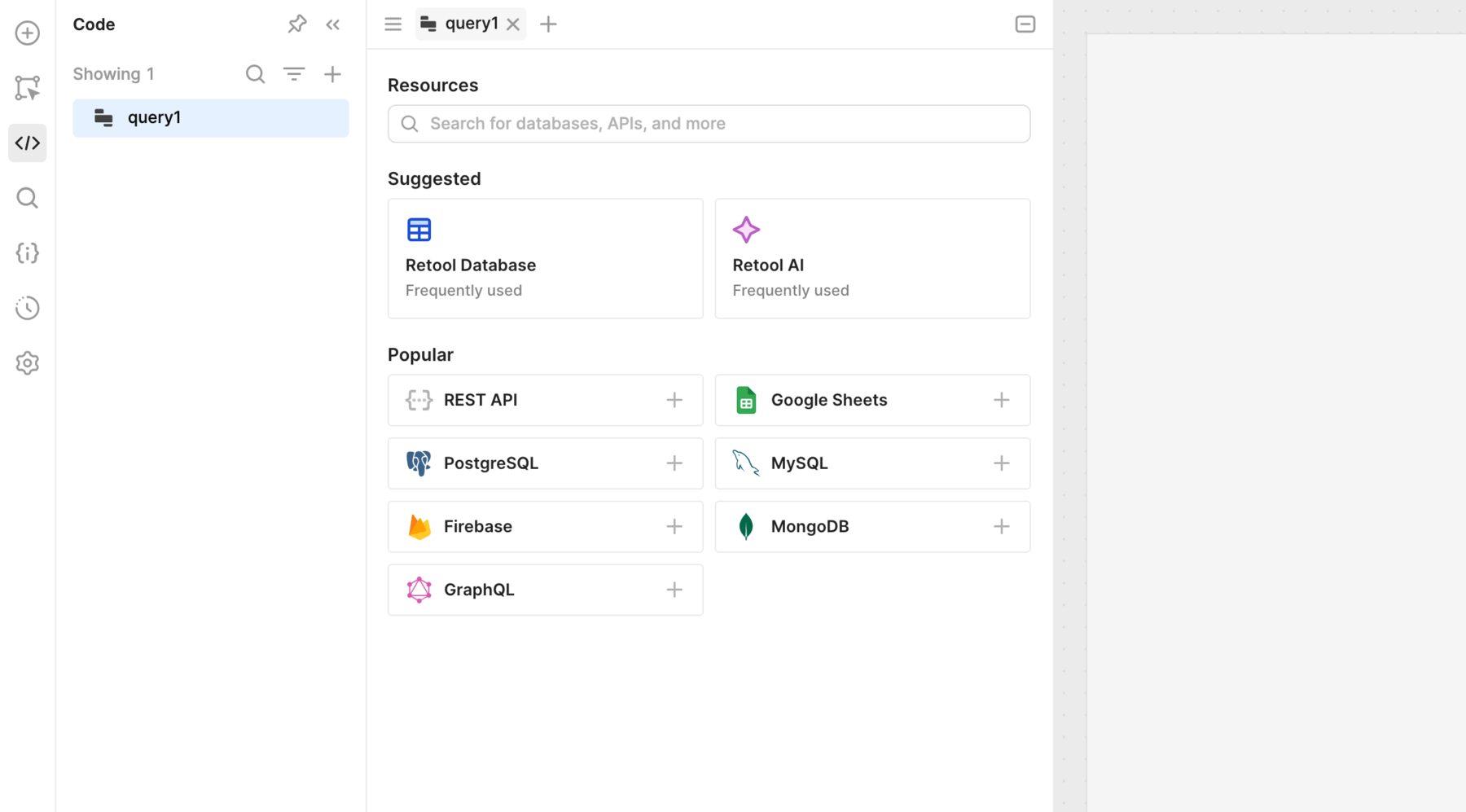
Query JSON data with SQL statements
Learn how to use SQL statements to query JSON data.
You can create queries that use SQL statements to query JSON data, such as data from other queries, using the Query JSON with SQL resource. Instead of referencing database tables for data, you use {{ }} to reference JSON arrays of objects.
Retool uses the AlaSQL JavaScript library for JSON SQL queries. Some SQL syntax may differ since queries run in the browser. For example, AlaSQL uses square brackets and backticks to enclose column names that contain whitespace, rather than double quotes.
Refer to the AlaSQL documentation for a complete reference on supported operations.
1. Add a query
- Web or mobile app
- Workflow
- Navigate to the Code tab in the IDE.
- Click + to add a new query.
- Select the Query JSON with SQL resource.
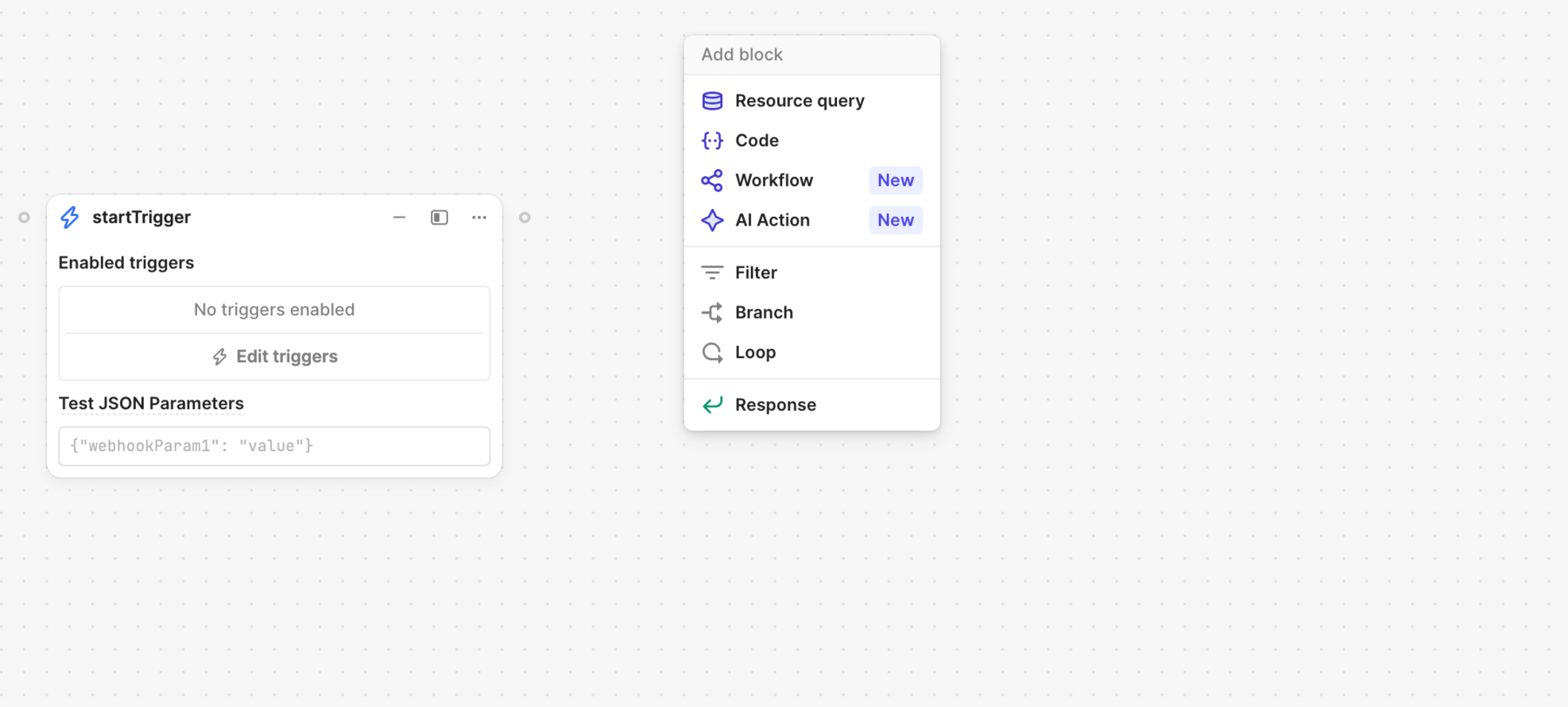
- Either:
- Right-click on the canvas and select the Resource query block.
- Click ⊕ in the left toolbar to open the Blocks tab, then select Resource query block.
- Click-and-drag from an existing block to create a new, connected block.
- Select the Query JSON with SQL resource.
2. Write an SQL statement
The structure of the data property depends on the response from the data source. Use the helper methods formatDataAsArray() or formatDataAsObject() to convert between arrays and objects.
- Web or mobile app
- Workflow
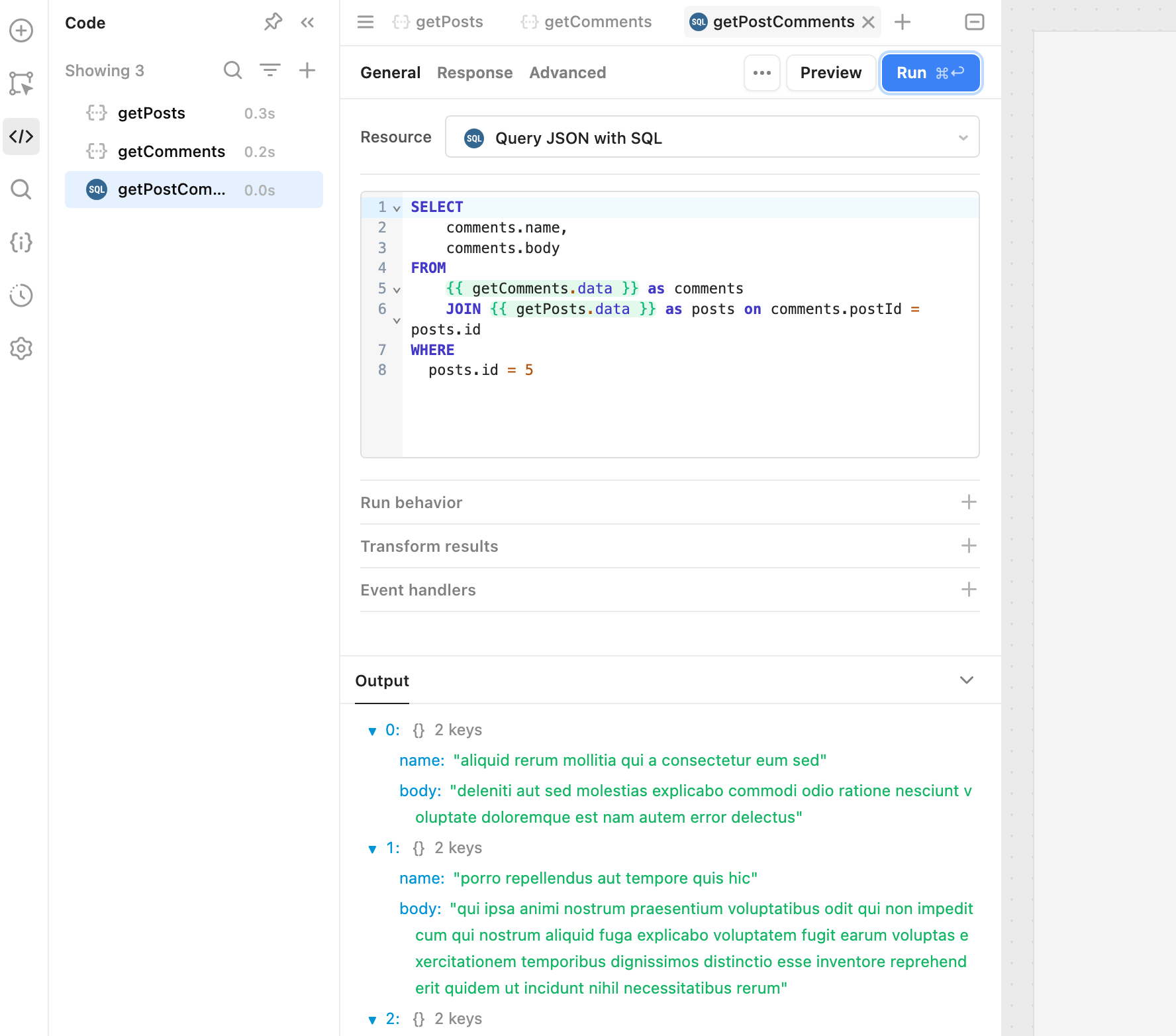
Resource queries, such as database queries or API requests, have a data property with retrieved data. You can reference this property when writing an SQL statement using {{ }} , such as {{ query.data }}.
You can also perform SQL joins when querying JSON. This allows you to combine and query APIs and other data sources.
The following example queries data from two separate API requests for posts and comments. The SQL statement uses a JOIN to connect the data together. The end result is a query that can retrieve comments for the specified post.
SELECT
comments.name,
comments.body
FROM
{ { getComments.data } } as comments
JOIN { { getPosts.data } } as posts on comments.postId = posts.id
WHERE
posts.id = 5
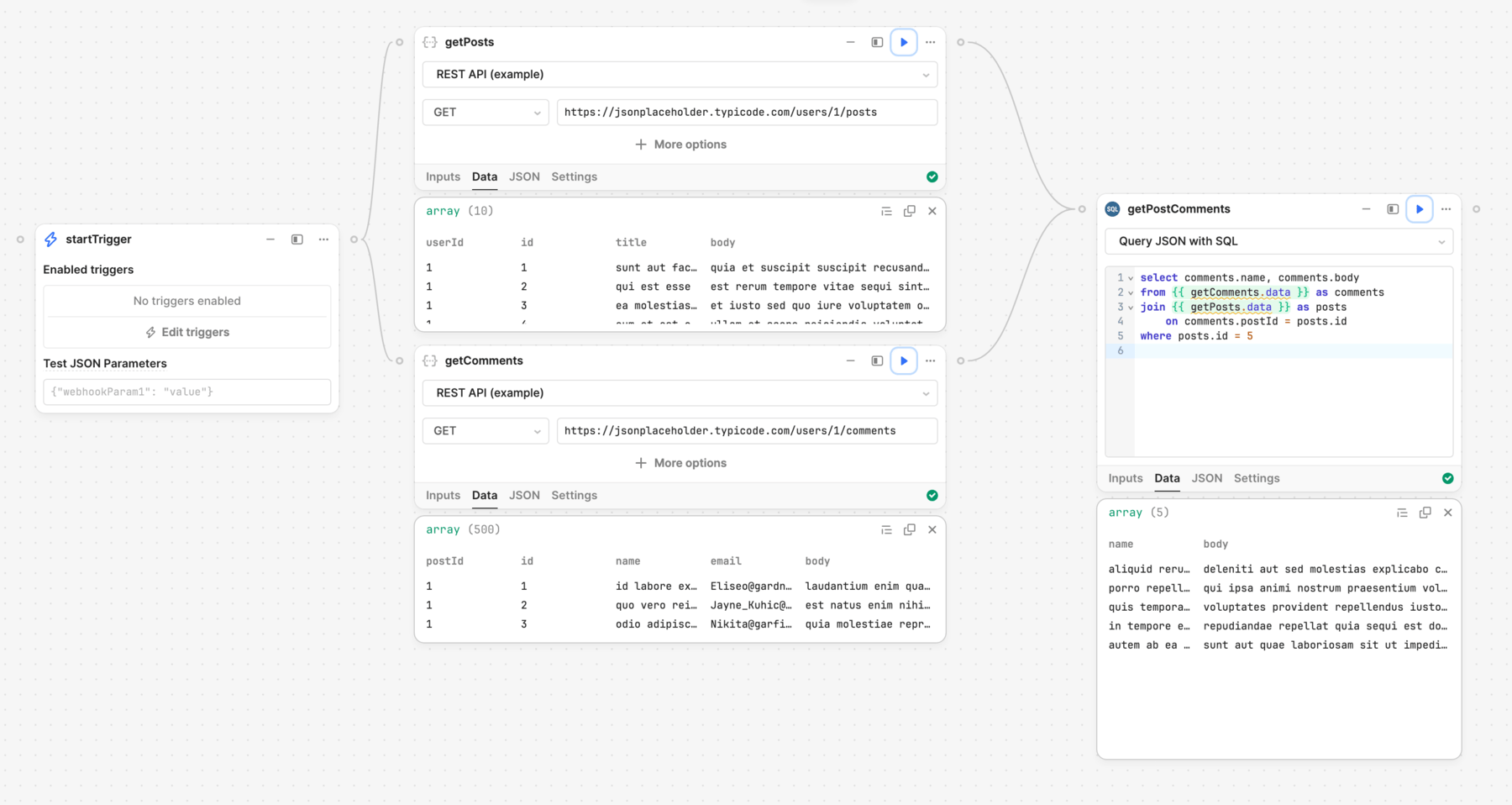
Resource queries, such as database queries or API requests, have a data property with retrieved data. You can reference this property when writing an SQL statement using {{ }} , such as {{ query.data }}.
You can also perform SQL joins when querying JSON. This allows you to combine and query APIs and other data sources.
The following example queries data from two separate API requests for posts and comments. The SQL statement uses a JOIN to connect the data together. The end result is a query that can retrieve comments for the specified post.
SELECT
comments.name,
comments.body
FROM
{ { getComments.data } } as comments
JOIN { { getPosts.data } } as posts on comments.postId = posts.id
WHERE
posts.id = 5
3. Run the query
- Web or mobile app
- Workflow
Click Save & Run to save the query and then execute it. The query results then appear in the Output tab.
You can reference the query output elsewhere in the app using the query's data property. This contains an object with key names that correspond to the column names. Each key contains an array of values.
Click ▶︎ to run the block. The query results then appear in the Data and JSON tabs.
You can reference the query output further down the control flow using the query's data property. This contains an object with key names that correspond to the column names. Each key contains an array of values.
Reference array values in JSON SQL queries
If you need to reference an array within a query, such as a list of values for an IN clause, prefix the array with @.
SELECT
id,
name,
subscription,
expiration
FROM
{{ formatDataAsArray(getUsers.data) }}
WHERE
id IN @({{ activeUsers.data }})