Read data from SQL databases
Learn how to construct queries to retrieve data from SQL databases and similar data stores.
You can create queries that use SQL statements to retrieve (read) data from connected database resources, such as a PostgreSQL or a MySQL database.
- Web or mobile app
- Workflow
1. Add a query
- Web or mobile app
- Workflow
- Navigate to the Code tab in the IDE.
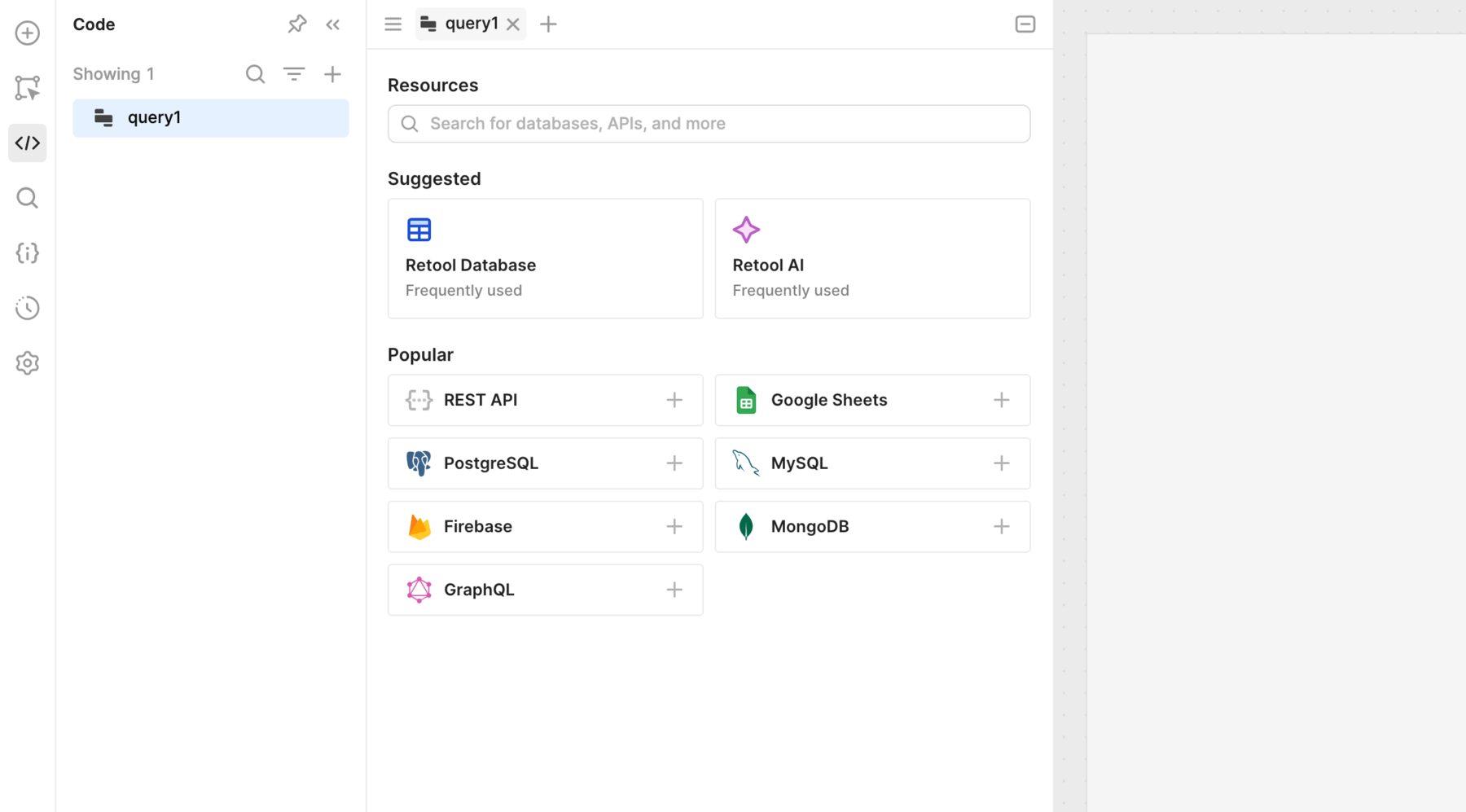
- Click + to add a new query.
- Select the resource.
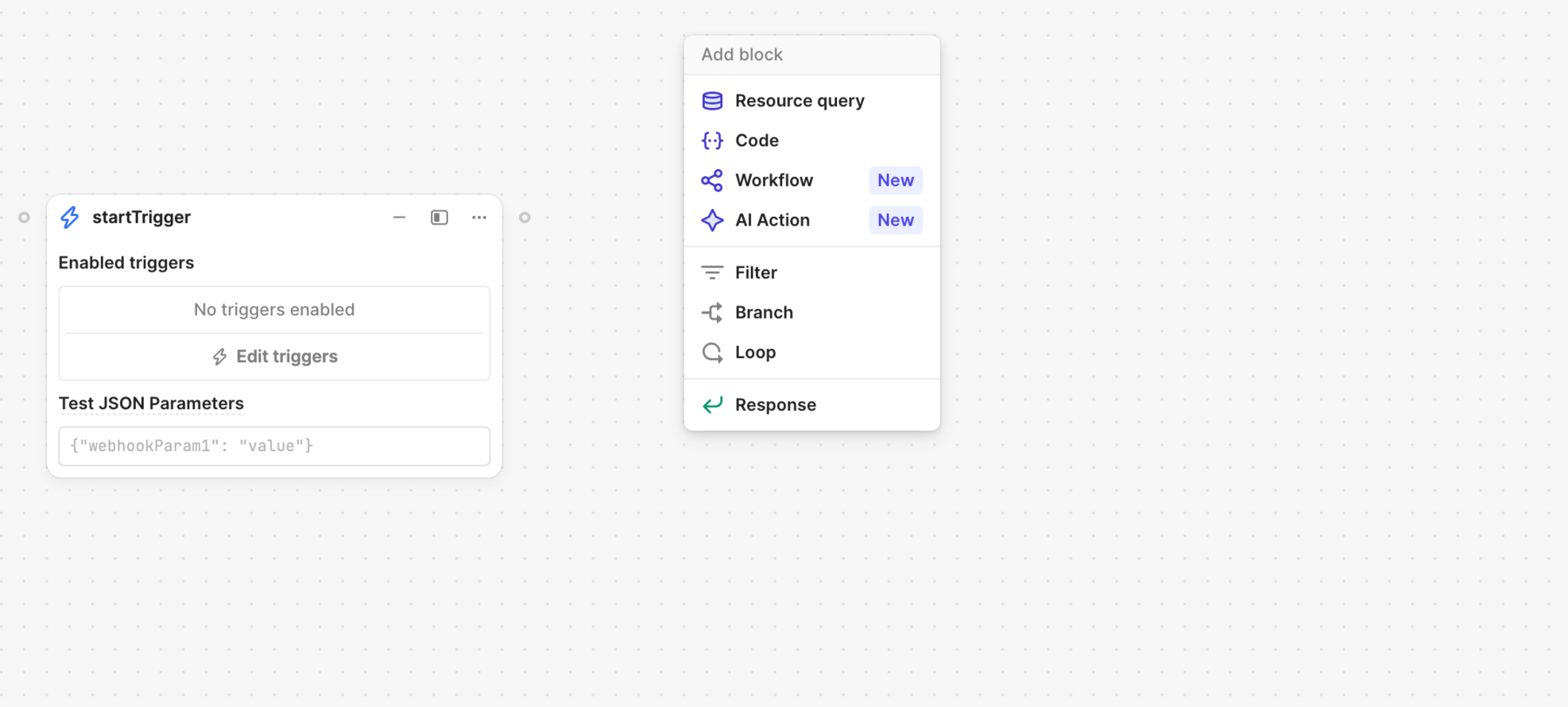
- Either:
- Right-click on the canvas and select the Resource query block.
- Click ⊕ in the left toolbar to open the Blocks tab, then select Resource query block.
- Click-and-drag from an existing block to create a new, connected block.
- Select the resource.
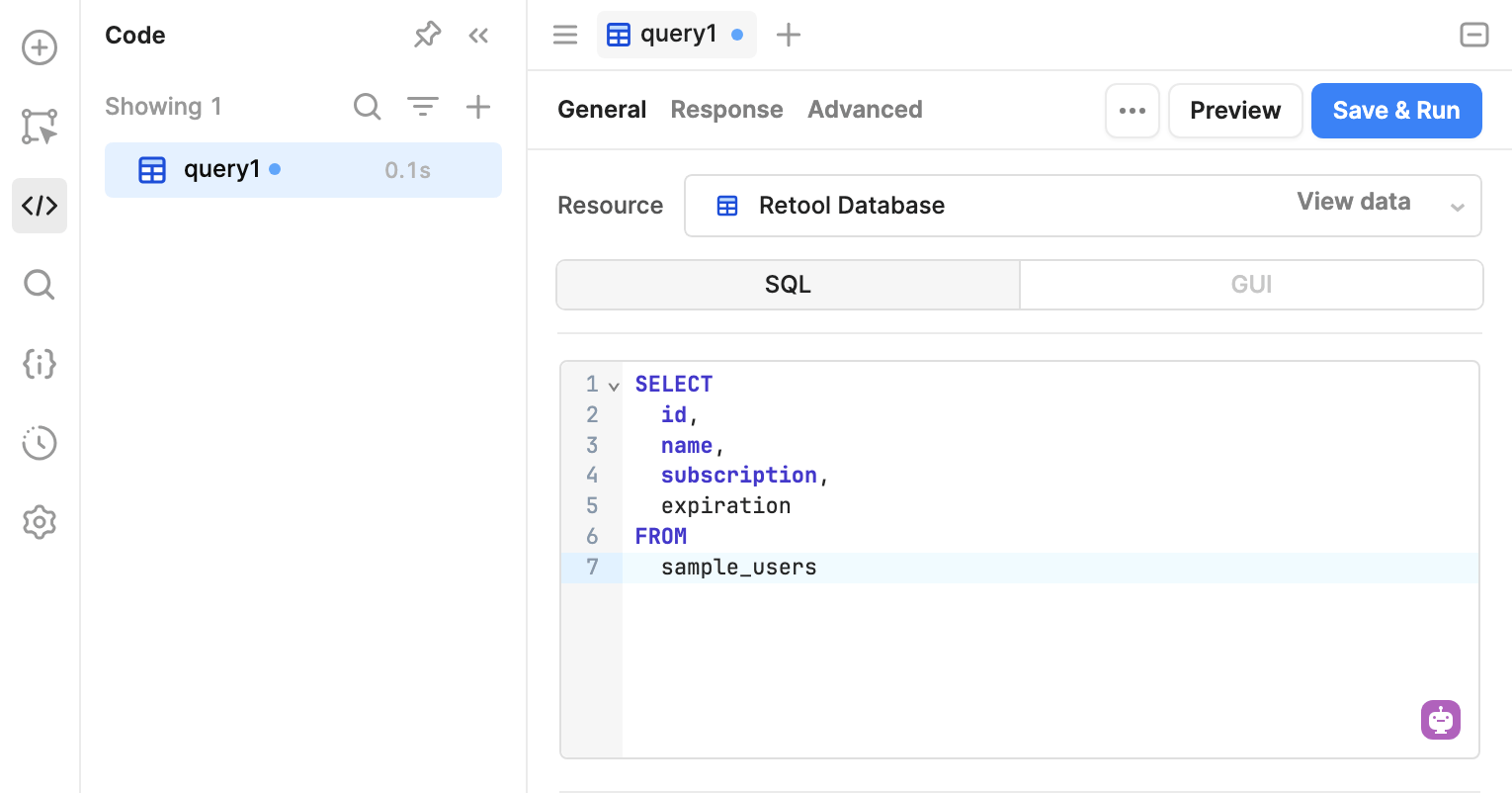
There are two modes from which to select when writing an SQL query. The mode you choose depends on whether you need to read or write data:
- SQL: Read data using an SQL statement.
- GUI: Write data using a graphical query editor.
Select SQL mode.
2. Write an SQL statement to retrieve data
You can also use the Ask AI option to generate SQL queries.
- Web or mobile app
- Workflow
Write an SQL statement to retrieve data from the database. The following example retrieves the id, name, subscription, and expiration values for all records in the sample_users table of a database.
SELECT
id,
name,
subscription,
expiration
FROM
sample_users
You use {{ }} to reference other values within the SQL statement, such as components and queries.
The following example adds a WHERE clause to retrieve only records with an expiration date prior to a Date Input component value.
SELECT
id,
name,
subscription,
expiration
FROM
sample_users
WHERE
expiration < {{ date1.value }}
Write an SQL statement to retrieve data from the database. The following example retrieves the id, name, subscription, and expiration values for all records in the sample_users table of a database.
SELECT
id,
name,
subscription,
expiration
FROM
sample_users
You use {{ }} embedded expressions to reference other values, such as blocks or webhook payloads.
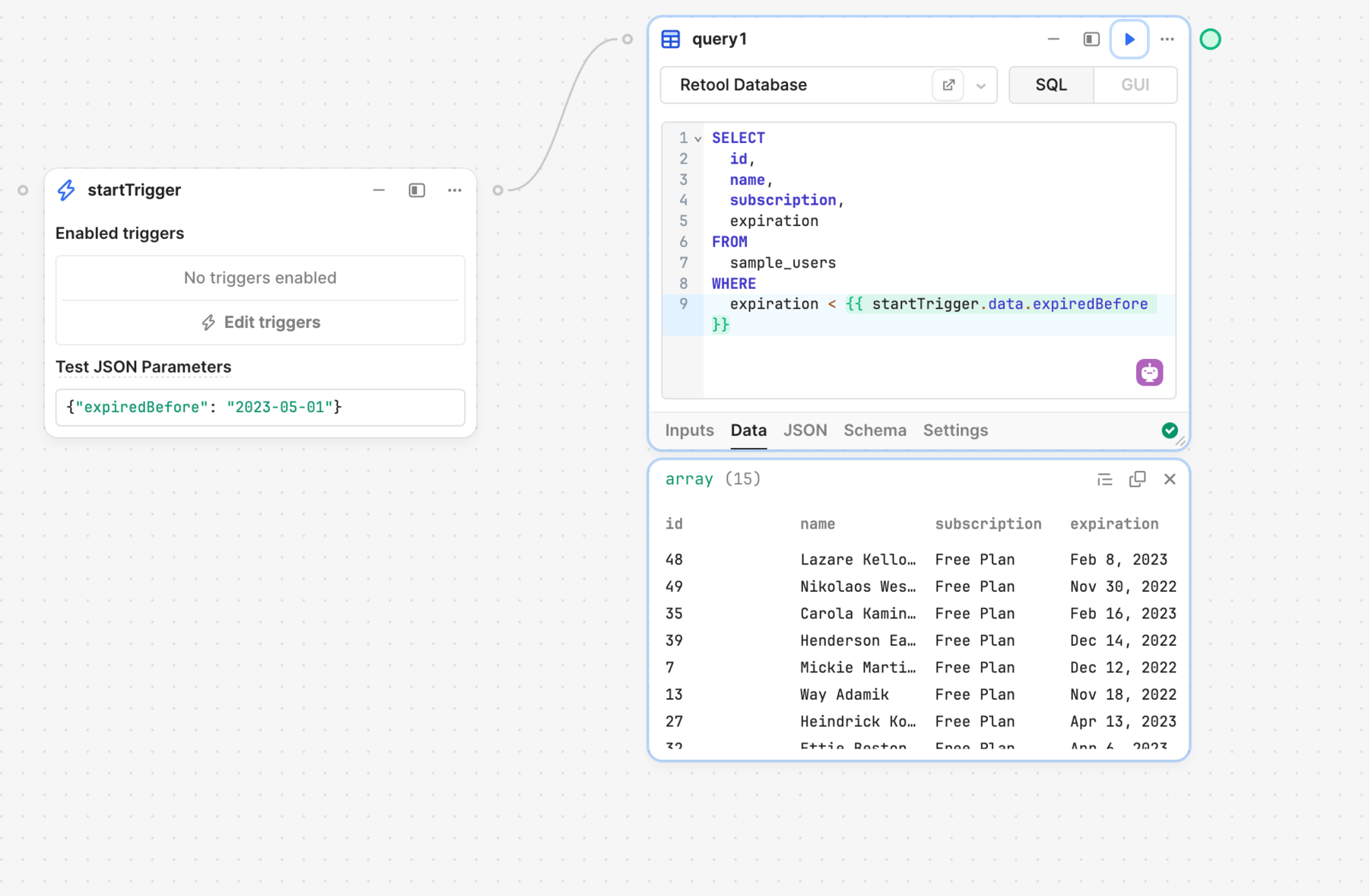
The following example adds a WHERE clause to retrieve only records with an expiration date before the expiredBefore value provided by the Start block.
SELECT
id,
name,
subscription,
expiration
FROM
sample_users
WHERE
expiration >= {{ moment() }}
AND expiration <= { { moment().add(1, 'days') } }
To prevent SQL injection, Retool converts SQL queries into prepared statements that separate the query from values. This prevents you from writing queries that dynamically reference column or table names.
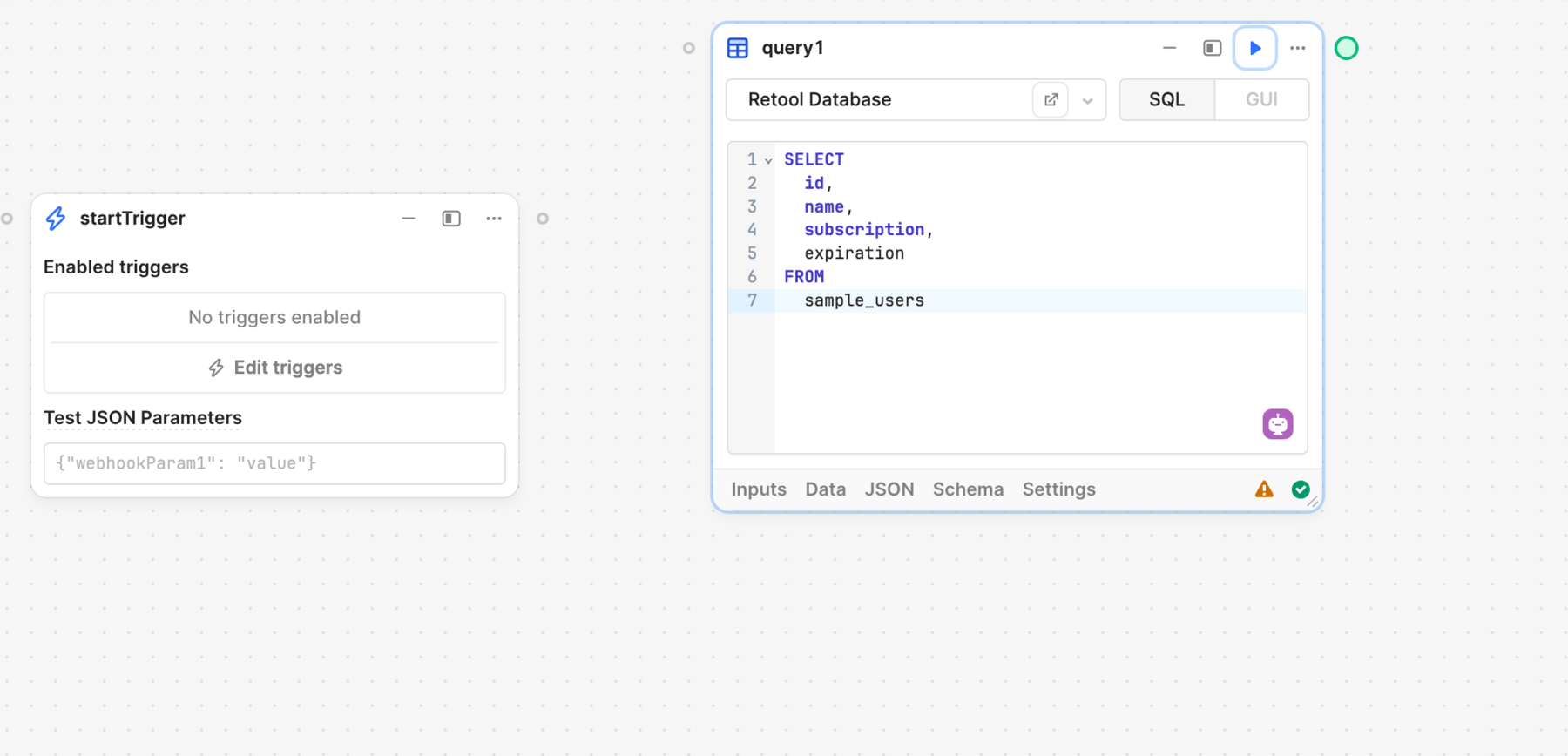
3. Run the query
- Web or mobile app
- Workflow
Click Save & Run to save the query and then execute it. The query results then appear in the Output tab.
You can reference the query output elsewhere in the app using the query's data property. This contains an object with key names that correspond to the column names. Each key contains an array of values.
Click ▶︎ to run the block. The query results then appear in the Data and JSON tabs.
You can reference the query output further down the control flow using the query's data property. This contains an object with key names that correspond to the column names. Each key contains an array of values.