Configure Source Control with GitHub
Learn how to set up Source Control with GitHub.
| Source Control Availability | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud | Generally Available | ||
| Self-hosted Edge 3.33 or later | Generally Available | ||
| Self-hosted Stable 3.33 or later | Generally Available | ||
You can use Source Control with GitHub to manage changes using pull requests. You create a repository for Source Control to use, then configure a GitHub App for your Retool instance that commits, pushes, and pulls changes.
Requirements
To configure Source Control with GitHub, you must have:
- Administrator permissions in your Retool organization.
- Permissions to create an app in GitHub.
1. Create a Git repository
Use a new, dedicated Git repository. Source Control does not work with an existing Git Syncing repository.
To begin, create a new repository for Source Control. Ensure it contains a README.md file and a main branch. Source Control uses this repository to store and track all changes.
If you have multiple Retool instances, use this same repository across all instances.
2. Create and install a GitHub App
Create a GitHub App with the following settings. Ensure this app is created by the same owner as the Git repository. Refer to GitHub's guide for more information.
If you have multiple Retool instances, use this same GitHub App across all instances.
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| GitHub App name | The name of your GitHub App. |
| Homepage URL | The URL of your GitHub App. This field is unused by Retool. |
| Expire user authorization tokens | Unchecked |
| Request user authorization (OAuth) during installation | Unchecked |
| Webhook > Active | Unchecked |
| Permissions > Contents | Read and write |
| Permissions > Pull requests | Read and write |
| Where can this GitHub App be installed? | Only on this account |
Install the GitHub App
After you create your GitHub App, it should appear in the GitHub Apps section of your Developer Settings.
To install your GitHub App:
- Click Edit next to your app to see its settings.
- Click on Install App.
- Click the Install button next to your organization.
- Choose the Only select repositories option and select the repository created in the first section.
- You’ll be redirected to the installation page. The number at the end of the URL is the installation ID. Save this for later.
https://github.com/settings/installations/:installation_id
Save the app owner and app ID
On the same page, click on App settings underneath the GitHub App name. Save the Owned by and App ID fields for later.
3. Generate a private key
- Navigate to the Private Keys section and click Generate a private key.
- Download and save the
.pemkey. The filename should use the format{github-app-name}.YYYY-MM-DD.private-key.pem. - Base64-encode the contents of the file to use when configuring your instance. If you use Kubernetes Secrets, you must base64-encode this value twice:
base64 -i path/to/{github-app-name}.YYYY-MM-DD.private-key.pem > github-private-key.txt
4. Configure GitHub repository settings
Next, configure the GitHub repository in Retool.
- Cloud and self-hosted instances on version 3.18 and later
- Self-hosted instances on version 2.96 and later
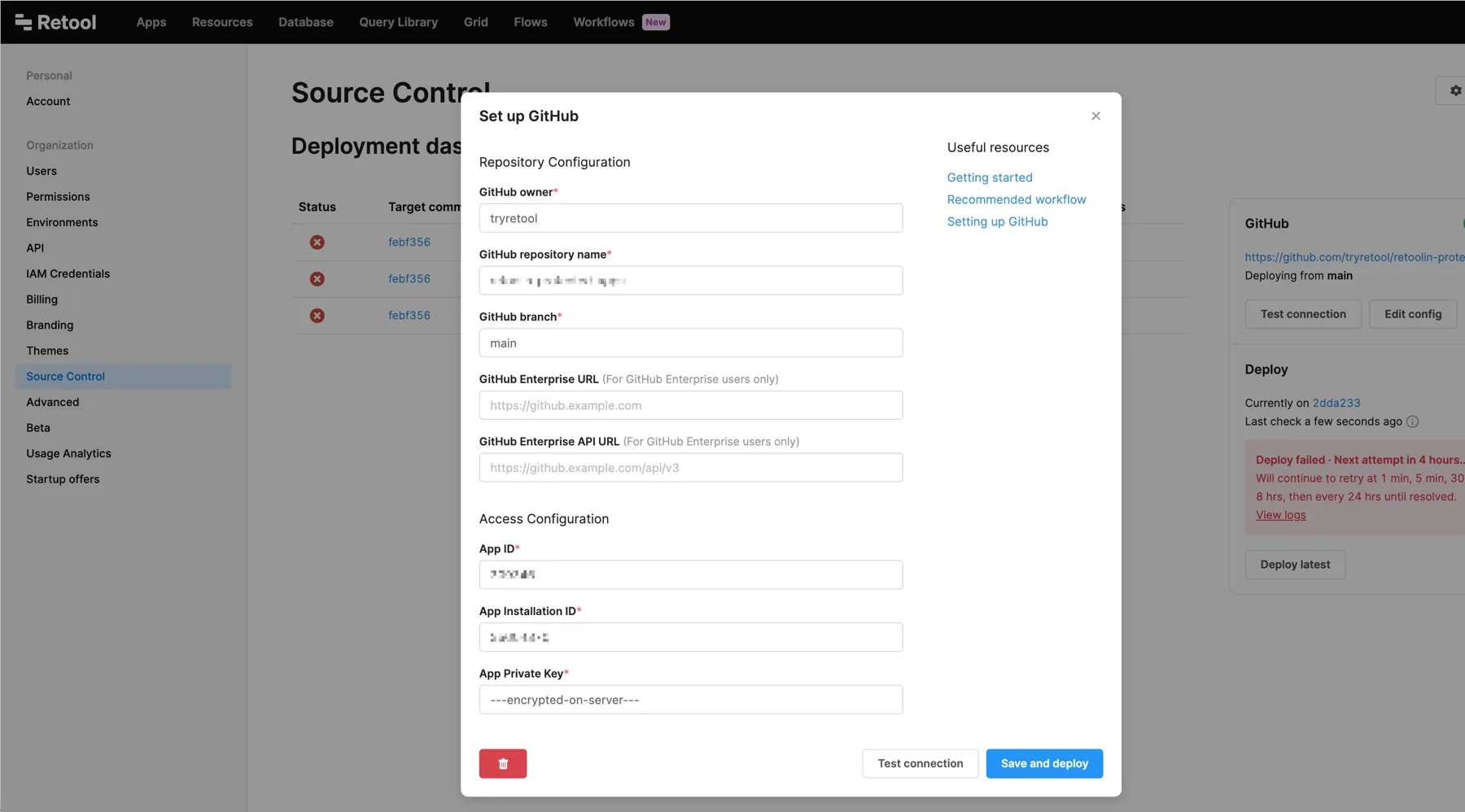
Navigate to the Source Control settings in Retool and select Set up GitHub.
Enter the settings using the details you saved when creating your GitHub app.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| GitHub owner | The username or organization who owns the GitHub App, without the @ prefix, e.g., tryretool. |
| GitHub repository | The name of the repository you created to use with Retool. |
| GitHub branch | The default branch, e.g., main. |
| GitHub Enterprise URL | The domain used to access your self-hosted GitHub instance. If you use GitHub Cloud, you can leave this blank. |
| GitHub Enterprise API URL | The REST API route for your self-hosted GitHub instance. Defaults to https://[hostname]/api/v3. If you use GitHub Cloud, you can leave this blank. |
| App ID | The GitHub App ID. |
| Installation ID | The GitHub installation ID. This can be found at the end of the installation URL. |
| App Private Key | The base64-encoded private key. |
You can choose to use a GitHub Personal Access Token for authentication instead of the GitHub app. To do so, navigate to Settings > Beta, and toggle on the GitHub Personal Access Token toggle. Return to the configuration page, and set Config type to Personal Access Token.
Click Test connection to confirm your app is connected, then click Save and deploy.
Configure the following Retool environment variables on the api and jobs-runner containers and then restart your containers.
| Environment variable | Description |
|---|---|
GITHUB_APP_ID | The GitHub App ID. |
GITHUB_APP_INSTALLATION_ID | The GitHub installation ID. This can be found at the end of the installation URL. |
GITHUB_APP_PRIVATE_KEY | The base64-encoded private key. |
If you use your own SSL certificates, set the SSL_CERT_FILE and NODE_EXTRA_CA_CERTS environment variables on the jobs-runner and api containers to the path to your SSL certificate.
Self-hosted instances using version 2.91 or later can optionally prevent the instance from pushing changes to GitHub. To lock version control, set the VERSION_CONTROL_LOCKED environment variable to true. This is useful for creating a "read-only" production instance of Retool.
For v2.97 and later, navigate to the Source Control settings and select Set up GitHub.
For v2.96 and earlier, navigate to the Advanced settings and select Protected Applications.
Enter the settings using the details you saved when creating your GitHub app.
| Setting | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GitHub owner | Yes | The username or organization who owns the GitHub App, without the @ prefix, e.g., tryretool. |
| GitHub repository | Yes | The name of the repository you created to use with Retool. |
| GitHub branch | Yes | The default branch, e.g., main. |
| GitHub Enterprise URL | No | The domain used to access your self-hosted GitHub instance. If you use GitHub Cloud, you can leave this blank. |
| GitHub Enterprise API URL | No | The REST API route for your self-hosted GitHub instance. Defaults to https://[hostname]/api/v3. If you use GitHub Cloud, you can leave this blank. |
Click Test connection to confirm your app is connected, then click Save and deploy.
Secure credential management
Sensitive credential fields, including App Private Key and Personal Access Tokens, support embedded expressions for secure credential management.
| Embedded expressions in Source Control credentials Availability | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud | Public beta | ||
| Self-hosted Edge 3.338 or later | Public beta | ||
| Self-hosted Stable Expected in Q2 2026 | |||
Toggle the Template variables in Source Control config feature flag in Settings > Beta to enable this feature.
- You can reference configuration variables:
{{ environment.variables.MY_KEY_OR_TOKEN }} - On self-hosted instances, you can also reference secrets from secrets managers:
{{ secrets.MY_SECRET.KEY }}
The UI includes autocomplete and validation to help you use embedded expressions correctly.
Troubleshooting
The following errors are issues common to Source Control with GitHub. Refer to the guide to resolve common Source Control issues to learn about other common errors.
Internal Server Error
If the system time on the machine that Retool is running on is out of sync or has "drifted," Retool can have trouble authenticating with the GitHub API.
If you see 500 Internal Server Error when making a commit on a branch, or see errors such as 'Issued at' claim ('iat') must be an Integer representing the time that the assertion was issued in Retool API server logs, check that the system time where the Retool image is running is accurate. Restarting the system can solve this issue.
Cookies must be enabled to use GitHub
This error occurs when the GitHub Enterprise API URL provided is not an API route. Check the URL provided and confirm that it is a GitHub API route.
Unable to access GitHub
If your Retool instance is behind a firewall and cannot access the GitHub API, add .github.com to your allowlist to enable outbound requests.