Configure Source Control with AWS CodeCommit
Learn how to set up Source Control with AWS CodeCommit.
| Source Control Availability | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud | Generally Available | ||
| Self-hosted Edge 3.33 or later | Generally Available | ||
| Self-hosted Stable 3.33 or later | Generally Available | ||
Setup instructions
Disable git syncing
If you've enabled Git Syncing, disable it:
- In your
docker.envfile, setDISABLE_GIT_SYNCING=trueandVERSION_CONTROL_LOCKED=false. - In the Settings > Advanced tab in Retool, remove the repository URL and branch name from your Git Syncing configuration.
1. Create a new IAM Role in your AWS account
Enter a name for the user and check the Access key - Programmatic access setting.
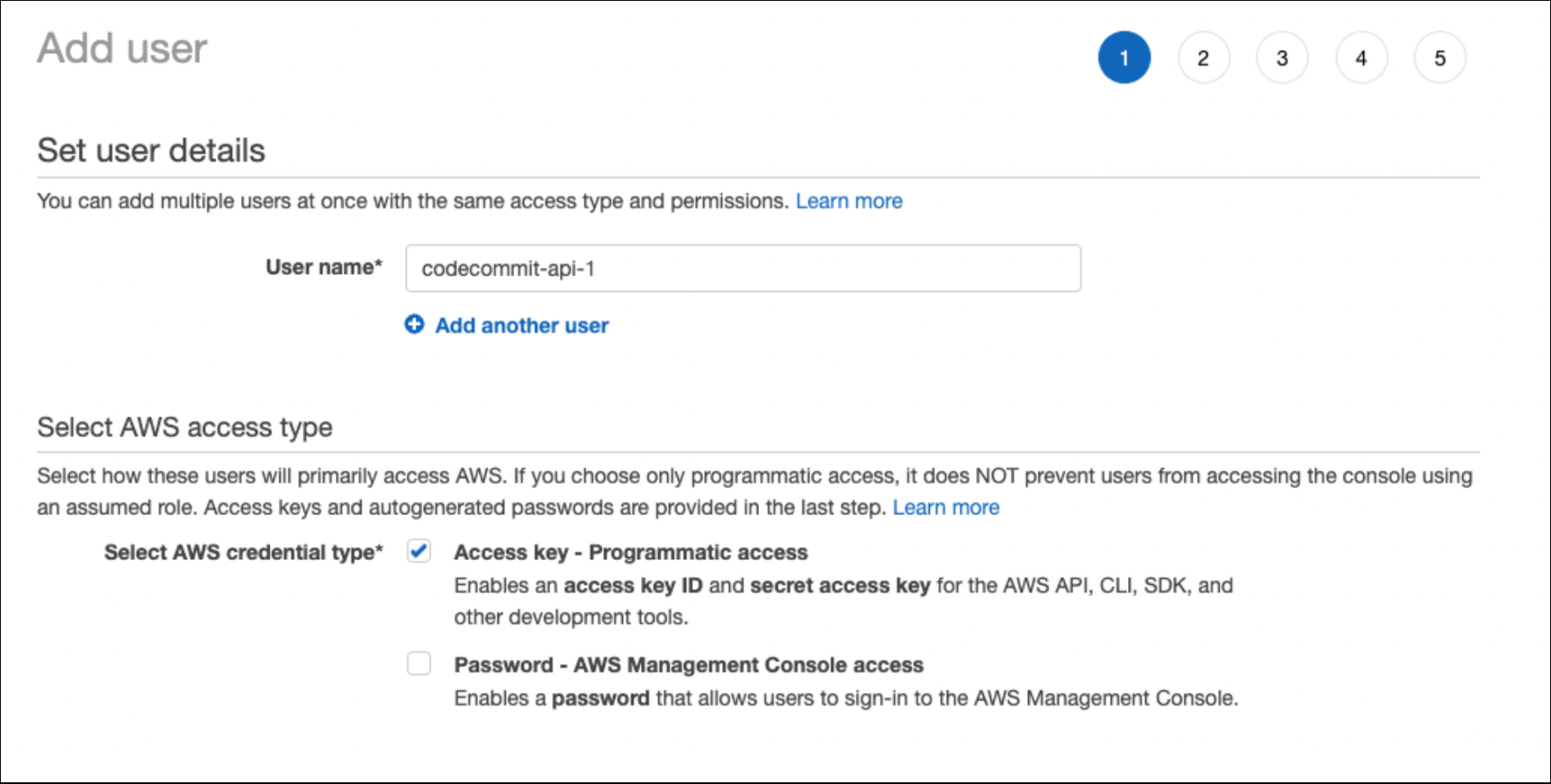
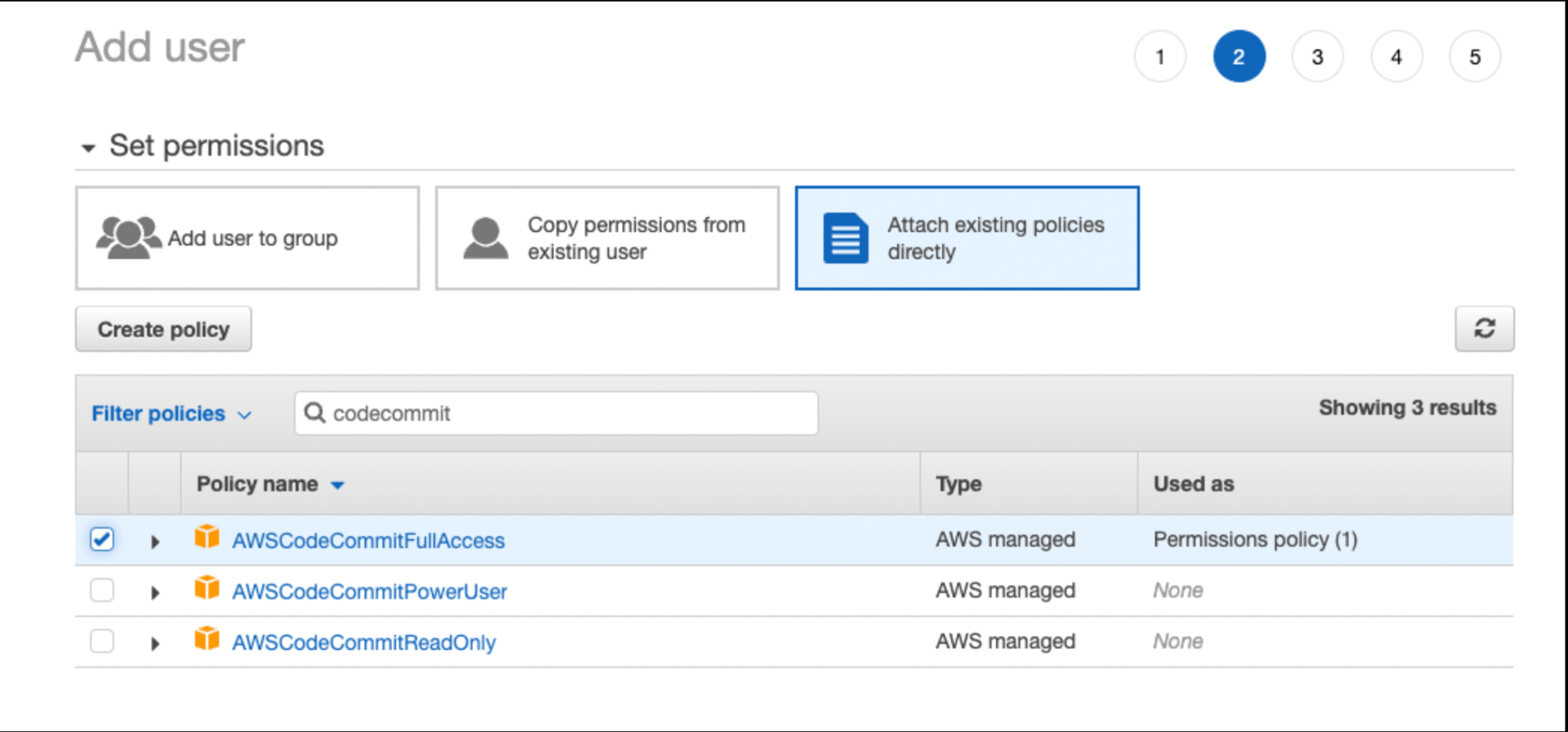
Next, select Attach existing policies directly, search for "codecommit", and select the AWSCodeCommitFullAccess policy name. This is the only permission required for this new user.
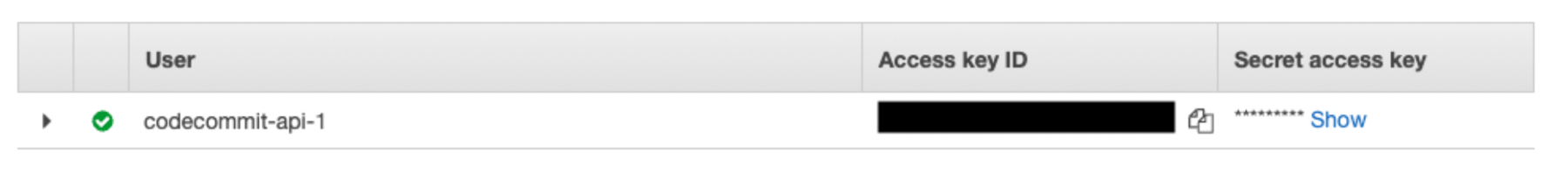
Save the Access key ID and Secret access key in a secure location locally. You'll use these as environment variables in step 3.
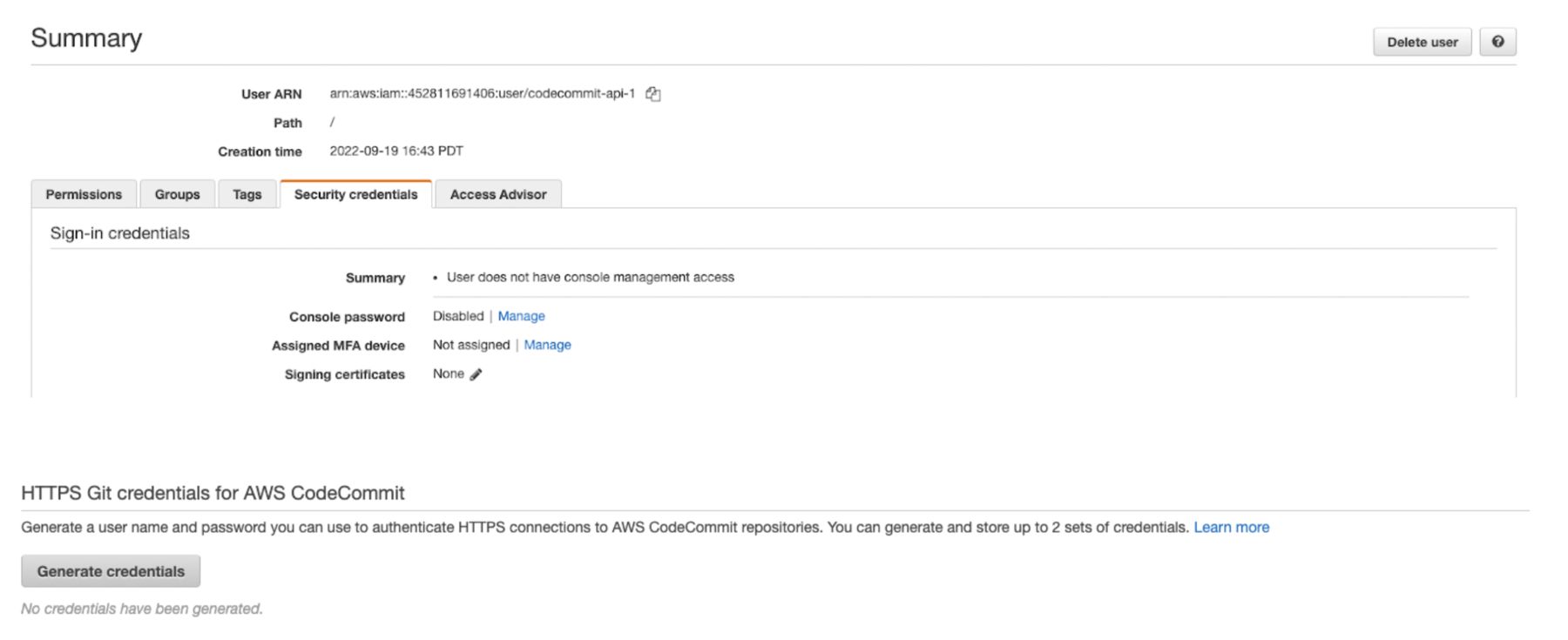
Go to the newly created user on your IAM console. Select the Security credentials tab, scroll to HTTPS Git Credentials for AWS CodeCommit, and click Generate Credentials. Download and save these credentials in a secure location. You'll use these HTTPS credentials as environment variables in step 3.
2. Create a new CodeCommit repository
Go to CodeCommit on your AWS console and create a new repository for Retool syncing. You can select any region of your preference.
Add a README.md file to this repository. The repository needs to contain at least one file to sync.
3. Configure AWS CodeCommit repository settings
- Cloud and self-hosted instances on version 3.18 and later
- Self-hosted instances on version 2.102 and later
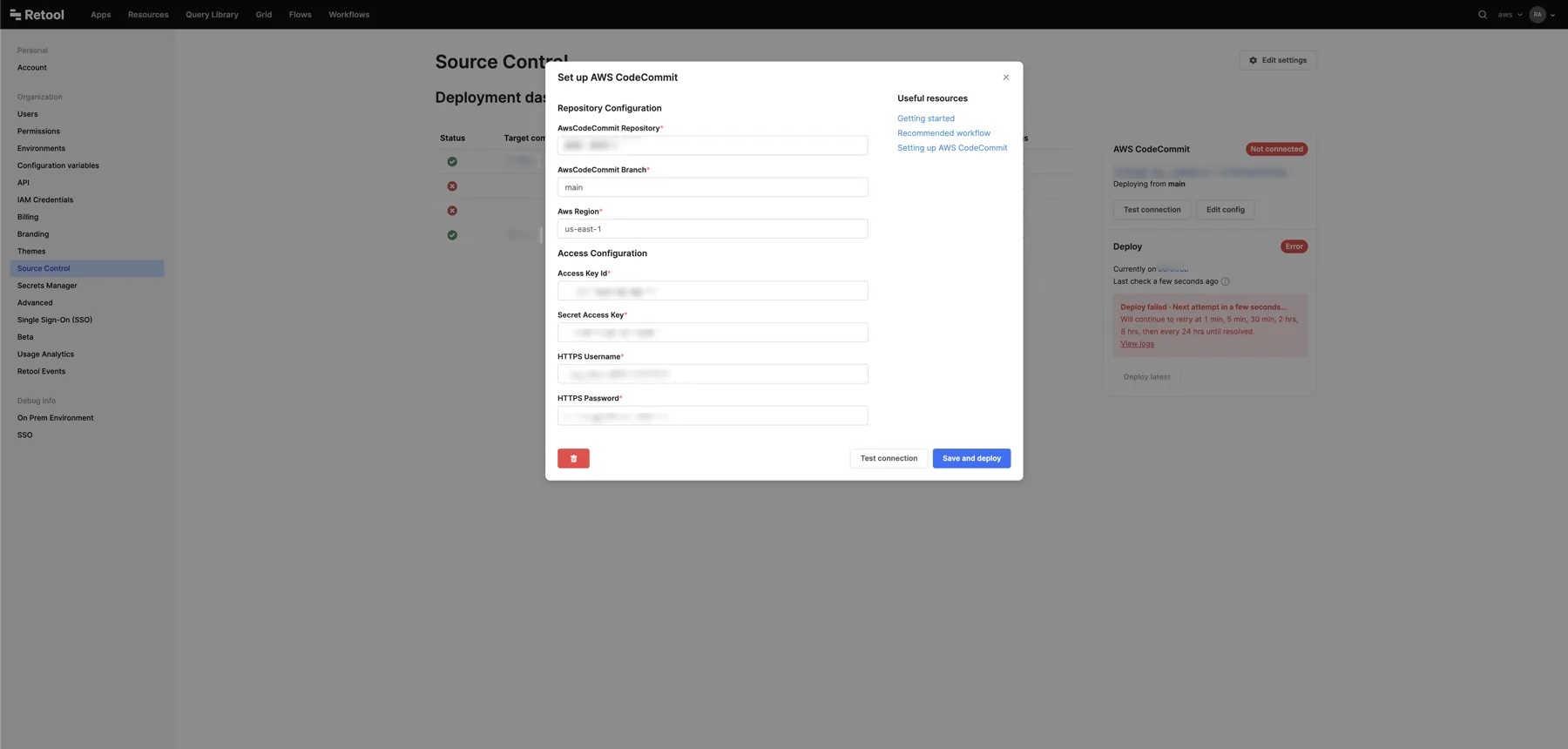
Go to the Source Control settings, and select Set up AWS CodeCommit. Enter the following settings.
| Setting | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| AWS CodeCommit Repository | The name of the CodeCommit repository. | retool-apps |
| AWS CodeCommit Branch | The default branch for your CodeCommit repository. | main |
| AWS Region | The region of the CodeCommit repository. | us-east-1 |
| Access Key Id | The Access key ID you generated in step 1. | AKIAWS3BACWHP6QW6VB2 |
| Secret Access Key | The Secret access key you generated in step 1. | loDJlwRetoolTYXOFbO |
| HTTPS Username | The HTTPS username you generated in step 1. | retool-https-username |
| HTTPS Password | The HTTPS password you generated in step 1. | retool-https-password |
Set the following environment variables on your Retool instance on the api and jobs-runner containers.
| Variable name | Description | Example value |
|---|---|---|
| CODE_COMMIT_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID | The Access key ID you generated in step 1. | AKIAWS3BACWHP6QW6VB2 |
| CODE_COMMIT_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY | The Secret access key you generated in step 1. | loDJlwRetoolTYXOFbO |
| CODE_COMMIT_AWS_DEFAULT_REGION | The region of the CodeCommit repository. | us-east-1 |
| CODE_COMMIT_REPOSITORY_NAME | The name of the CodeCommit repository. | retool-apps |
| CODE_COMMIT_MAIN_BRANCH | The default branch for your CodeCommit repository. | main |
| CODE_COMMIT_HTTPS_USERNAME | The HTTPS username you generated in step 1. | retool-https-username |
| CODE_COMMIT_HTTPS_PASSWORD | The HTTPS password you generated in step 1. | retool-https-password |
If you use your own SSL certificates, set the SSL_CERT_FILE and NODE_EXTRA_CA_CERTS environment variables on the jobs-runner and api containers to the path to your SSL certificate.
Secure credential management
Sensitive credential fields, including Access Key Id, Secret Access Key, HTTPS Username, and HTTPS Password, support embedded expressions for secure credential management.
| Embedded expressions in Source Control credentials Availability | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud | Public beta | ||
| Self-hosted Edge 3.338 or later | Public beta | ||
| Self-hosted Stable Expected in Q2 2026 | |||
Toggle the Template variables in Source Control config feature flag in Settings > Beta to enable this feature.
- You can reference configuration variables:
{{ environment.variables.MY_KEY_OR_TOKEN }} - On self-hosted instances, you can also reference secrets from secrets managers:
{{ secrets.MY_SECRET.KEY }}
The UI includes autocomplete and validation to help you use embedded expressions correctly.
4. Verify your settings
After you set up your environment variables, visit the Settings > Source Control on your Retool instance.
If your environment is correctly configured, the page will show a Deployment Dashboard. Click Test connection under the AWS CodeCommit section to test your connection and confirm the sync works as expected.
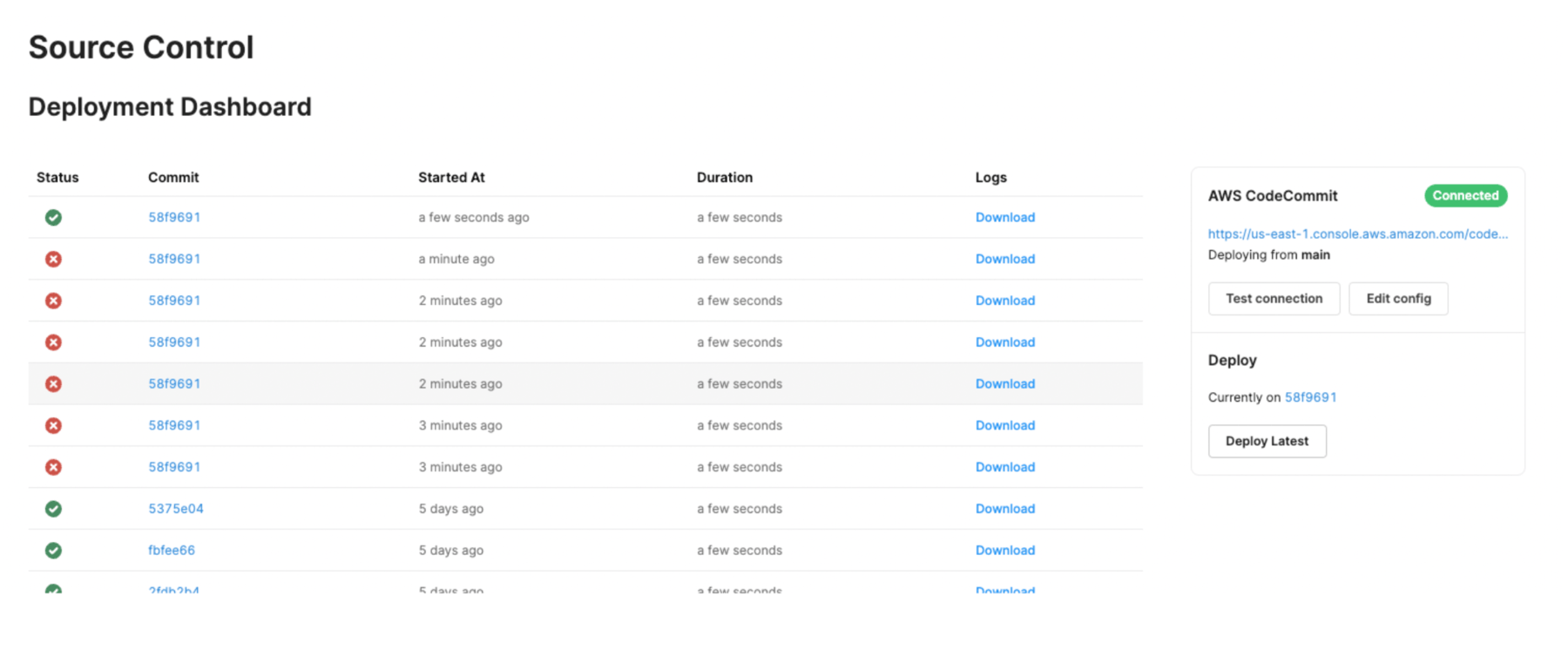
If you don't see the Deployment Dashboard and your AWS CodeCommit commits, go back to step 3 and confirm your environment variables are correctly set.
You are now ready to use source control with AWS CodeCommit. Read the source control getting started guide to learn more about source control workflows.