Configure Source Control with GitLab
Learn how to set up Source Control with GitLab for self-hosted instances.
| Source Control Availability | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud | Generally Available | ||
| Self-hosted Edge 3.33 or later | Generally Available | ||
| Self-hosted Stable 3.33 or later | Generally Available | ||
You can use Source Control with GitLab to manage changes using pull requests. You create a repository for Source Control to use, then configure a GitLab project for your Retool instance that commits, pushes, and pulls changes.
Source Control requires the use of GitLab project access tokens. See GitLab's documentation to verify you have access to these tokens.
Prerequisites
Self-hosted instances that currently use Git Syncing to sync with GitLab must disable this feature before switching to Source Control. To disable:
- Set
DISABLE_GIT_SYNCING=trueandVERSION_CONTROL_LOCKED=falsein thedocker.envfile. - Navigate to Settings > Advanced, then Remove the GitLab repository URL and branch name from your Git Syncing configuration.
1. Create a GitLab project
Create a new project on GitLab. This project repository stores the apps under Source Control from your Retool deployment. Use the following settings:
- Set the correct group under the Project URL dropdown.
- Select the Initialize repository with a README checkbox.
Next, follow GitLab's Project access token documentation to create an access token. Set the following scopes for the token:
apiread_apiread_repositorywrite_repository.
Set the role to maintainer or developer.
2. Configure settings in Retool
Configure the GitLab repository settings.
Ensure your GitLab domain contains an IPv6 (AAAA) DNS record to prevent server errors when Retool attempts to connect to your GitLab instance.
You can confirm whether you have IPv6 configured by running:
dig <domain name> AAAA
If the output of the command is ANSWER: 0, then the IPv6 DNS record is missing.
- Cloud and self-hosted instances on version 3.18 and later
- Self-hosted instances on version 112 and later
- Self-hosted instances on version 111 and earlier
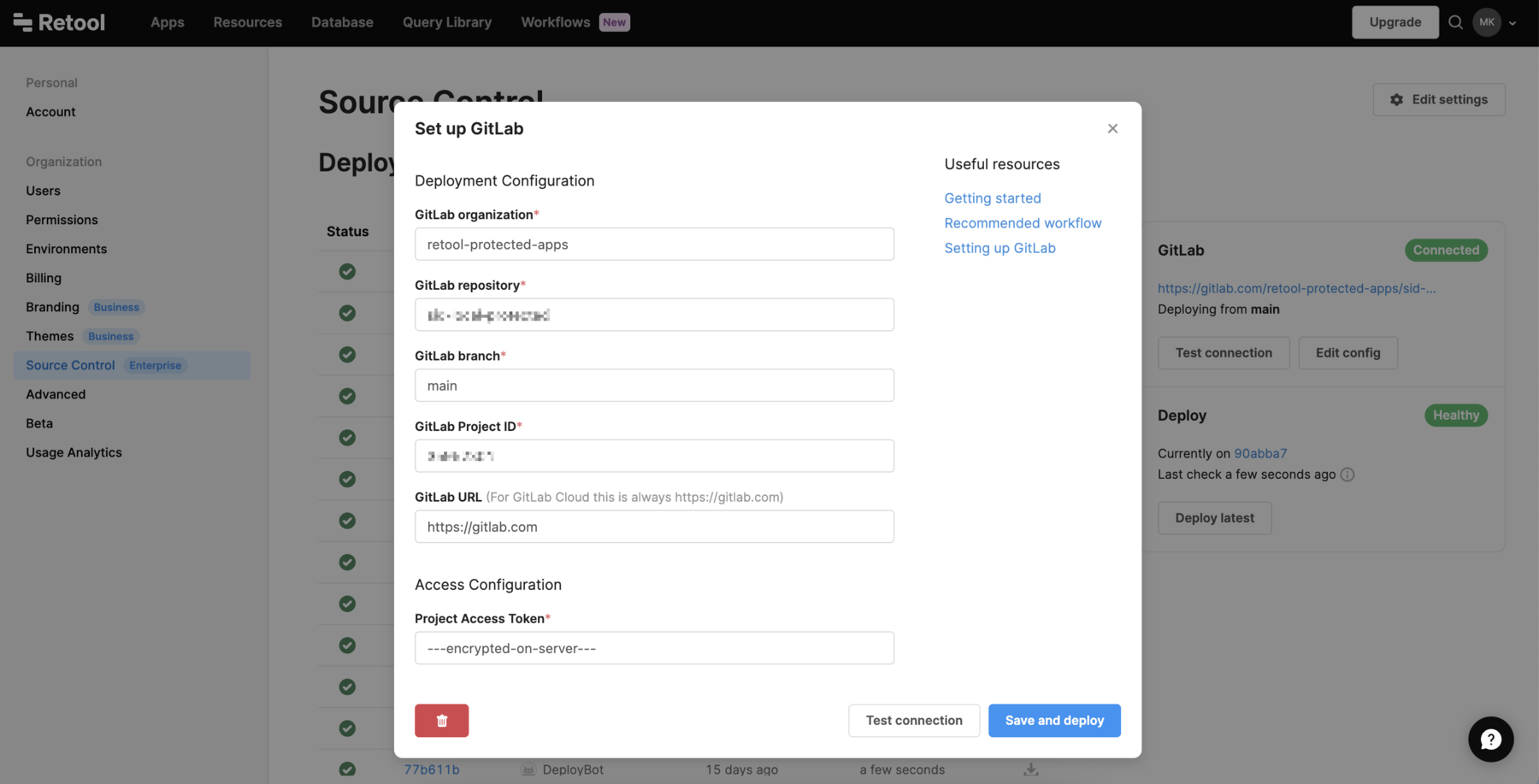
Go to the Source Control settings, and select Set up GitLab. Enter the following settings.
| Setting | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| GitLab URL | Your base GitLab URL. On GitLab Cloud, this is always https://gitlab.com. On GitLab self-managed, this is the URL where your instance is hosted. | https://gitlab.mycompany.com |
| Project access token | The GitLab project access tokens to authenticate to the GitLab API. | glpat-123xyzabc456 |
| GitLab project ID | The numerical project ID for your GitLab project. Find this ID listed below the project's name on the project's homepage. | 278964 |
| GitLab branch | The default branch for your GitLab project. | main |
| GitLab organization | The name of your GitLab organization. This can be a username if the project is not part of an organization. | company, username, engineering, etc. |
| GitLab repository | The name of the GitLab project. | retool-apps |
Set the following environment variables on your api and jobs-runner containers.
| Environment variable | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
GITLAB_PROJECT_ACCESS_TOKEN | The GitLab project access tokens to authenticate to the GitLab API. | glpat-123xyzabc456 |
If you use your own SSL certificates, set the SSL_CERT_FILE and NODE_EXTRA_CA_CERTS environment variables on the jobs-runner and api containers to the path to your SSL certificate.
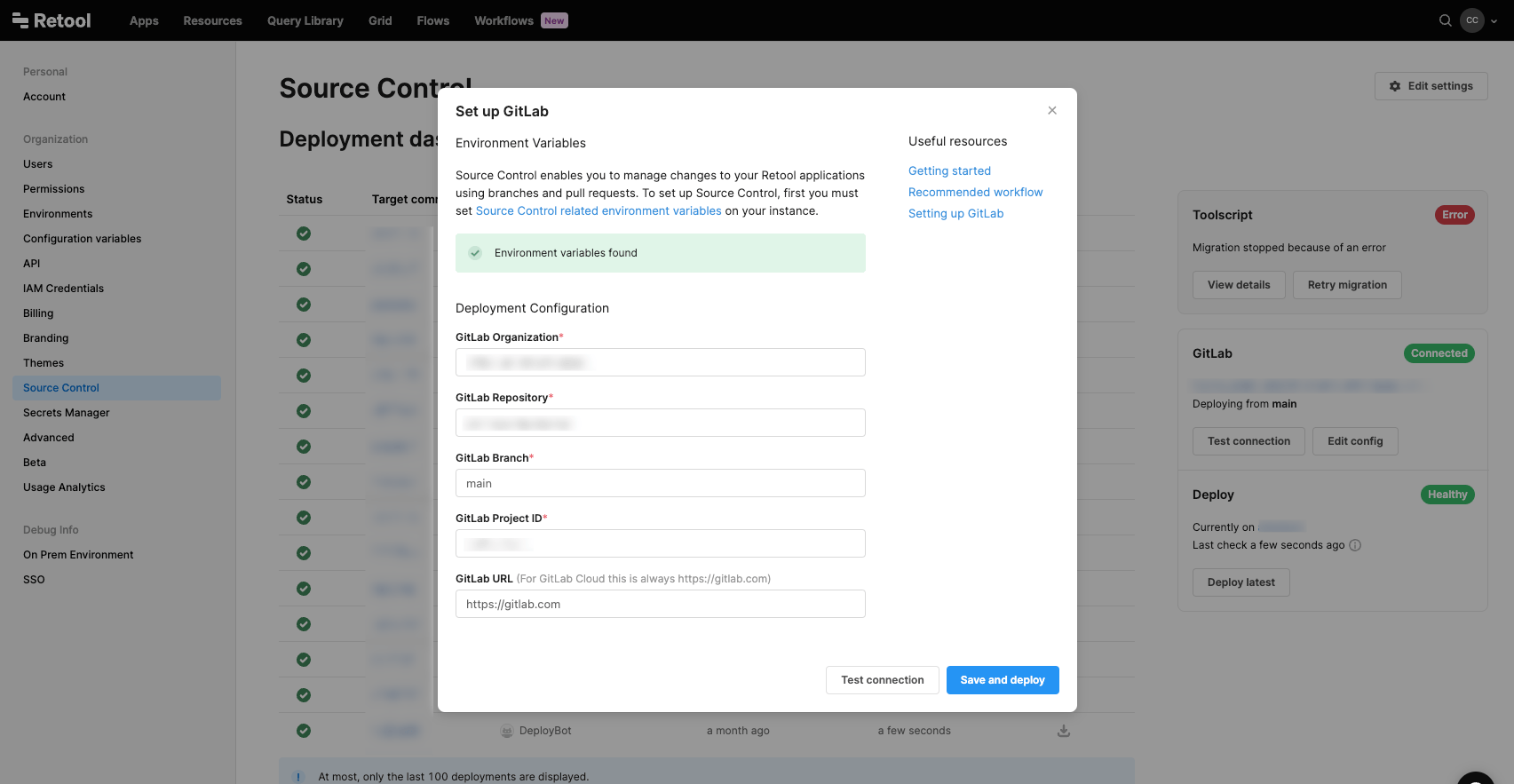
Go to the Source Control settings, and select Set up GitLab.
| Setting | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| GitLab URL | Your base GitLab URL. For GitLab Cloud, this is always https://gitlab.com. For GitLab self-managed, this is the URL where your instance is hosted. | https://gitlab.mycompany.com |
| GitLab project ID | The numerical project ID for your GitLab project. Find this ID listed below the project's name on the project's homepage. | 278964 |
| GitLab branch | The default branch for your GitLab project. | main |
| GitLab organization | The name of your GitLab organization. This can be a username if the project is not part of an organization. | company, username, engineering, etc. |
| GitLab repository | The name of the GitLab project. | retool-apps |
Set the following environment variables on your api and jobs-runner containers.
| Environment variable | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
GITLAB_URL | Your base GitLab URL. For GitLab Cloud, this is always https://gitlab.com. For GitLab self-managed, this is the URL where your instance is hosted. | https://gitlab.mycompany.com |
GITLAB_PROJECT_ACCESS_TOKEN | The GitLab project access tokens to authenticate to the GitLab API. | glpat-123xyzabc456 |
GITLAB_PROJECT_ID | The numerical project ID for your GitLab project. Find this ID listed below the project's name on the project's homepage. | 278964 |
GITLAB_MAIN_BRANCH | The default branch for your GitLab project. | main |
GITLAB_ORGANIZATION_NAME | The name of your GitLab organization. This can be a username if the project is not part of an organization. | company, username, engineering, etc. |
GITLAB_REPOSITORY_NAME | The name of the GitLab project. | retool-apps |
GITLAB_PROJECT_SLUG | The URL path to your GitLab project. | retool/eng/retool-apps |
VERSION_CONTROL_LOCKED | When set to true, the instance becomes a "read-only" instance and users cannot create or edit apps. Available on Retool versions 2.91 and later. | false |
If you use your own SSL certificates, set the SSL_CERT_FILE and NODE_EXTRA_CA_CERTS environment variables on the jobs-runner and api containers to the path to your SSL certificate.
Your Retool instance uses GitLab-specific environment variables to recreate the host URL for your GitLab project. You must provide values for either GITLAB_ORGANIZATION_NAME and GITLAB_REPOSITORY_NAME, or GITLAB_PROJECT_SLUG. For example, if your project URL is https://gitlab.com/retool-source/gitlab-retool-dev, you can set GITLAB_ORGANIZATION_NAME=retool-source and GITLAB_REPOSITORY_NAME=gitlab-retool-dev, or GITLAB_PROJECT_SLUG=retool-source/gitlab-retool-dev.
Secure credential management
The Project access token field supports embedded expressions for secure credential management.
| Embedded expressions in Source Control credentials Availability | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud | Public beta | ||
| Self-hosted Edge 3.338 or later | Public beta | ||
| Self-hosted Stable Expected in Q2 2026 | |||
Toggle the Template variables in Source Control config feature flag in Settings > Beta to enable this feature.
- You can reference configuration variables:
{{ environment.variables.MY_KEY_OR_TOKEN }} - On self-hosted instances, you can also reference secrets from secrets managers:
{{ secrets.MY_SECRET.KEY }}
The UI includes autocomplete and validation to help you use embedded expressions correctly.
3. Verify GitLab settings
On versions 2.97 and later, go to the Source Control settings page to verify your GitLab project is correctly configured. If you still see the Set up GitLab option, confirm your environment variables are set.
To confirm Retool can connect to your GitLab project, select Test connection.
On versions 2.96 and earlier, confirm GitLab is correctly set up by protecting your first application.
4. Save your settings
Click Save and deploy to save your settings.